We've learned how to identify inscribed and circumscribed angles. We've also learned how to apply the Inscribed Angle Theorem to circle problems. Complete these review questions to get ready for the lesson quiz. Review any concepts you find difficult.
1. Circle W has a center of point P and a radius of 5 units. Point Q is 4 units away from point P. Where is point Q?
- on circle W
- outside circle W
- inside circle W
- cannot be determined
If the distance between points P and Q is less than the radius of the circle, then point Q is inside circle W.
If the distance between points P and Q is less than the radius of the circle, then point Q is inside circle W.
If the distance between points P and Q is less than the radius of the circle, then point Q is inside circle W.
If the distance between points P and Q is less than the radius of the circle, then point Q is inside circle W.
2. Which angle is a circumscribed angle?
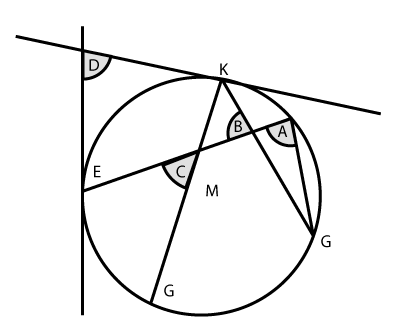
- Angle A
- Angle B
- Angle C
- Angle D
A circumscribed angle lies outside the circle and is formed by the intersection of two tangent lines.
A circumscribed angle lies outside the circle and is formed by the intersection of two tangent lines.
A circumscribed angle lies outside the circle and is formed by the intersection of two tangent lines.
A circumscribed angle lies outside the circle and is formed by the intersection of two tangent lines.
3. Which angle is an inscribed angle.

- Angle A
- Angle B
- Angle C
- Angle D
An inscribed angle has vertex that is on the circle and sides that are chords on the circle.
An inscribed angle has vertex that is on the circle and sides that are chords on the circle.
An inscribed angle has vertex that is on the circle and sides that are chords on the circle.
An inscribed angle has vertex that is on the circle and sides that are chords on the circle.
4. What is the measure of angle Z if the measure of arc NK is 134°?
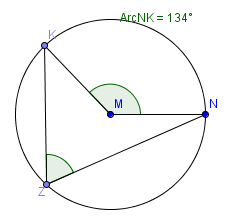
- 134°
- 67°
- 34°
- 268°
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
5. Arc K1 has endpoints N and K. What is the measure of arc K1 if the measure of angle Z is 52°?
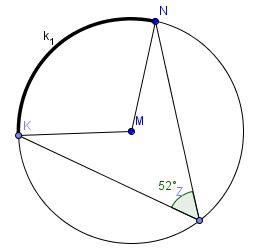
- 26°
- 52°
- 104°
- 158°
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
6. Find the value of y.
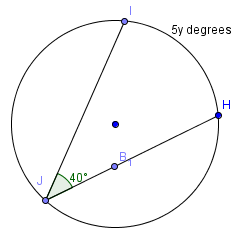
- 16
- 40
- 80
- 100
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
5y = 80
y = 16
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
5y = 80
y = 16
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
5y = 80
y = 16
The measure of an inscribed angle is ½ the measure of its associated intercepted arc.
5y = 80
y = 16
Summary
 Questions answered correctly:
Questions answered correctly:
 Questions answered incorrectly:
Questions answered incorrectly:
