Let's calculate the slope of our landing plane.
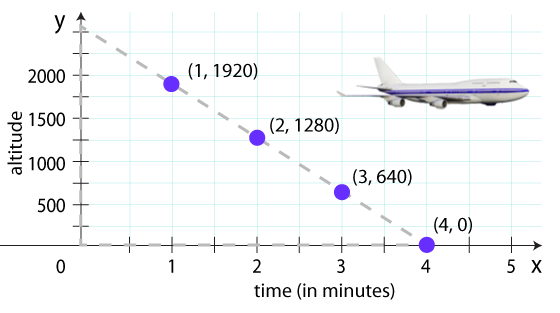
| x = Time (in minutes) | y = Feet |
| 1 | 1920 |
| 2 | 1280 |
| 3 | 640 |
| 4 | 0 |
Now let's calculate the rate of change, or slope. Remember that slope is calculated:
m = \(\mathsf{ \frac{\text{rise}}{\text{run}} }\)
| Time Span | Slope |
| (1, 1920) to (2, 1280) |
\(\mathsf{ \frac{\text{rise}}{\text{run}} = \frac{1280-1920}{2-1} = \frac{-640\text{ft}}{1\text{min}} }\) |
| (2, 1280) to (3, 640) |
\(\mathsf{ \frac{\text{rise}}{\text{run}} = \frac{640-1280}{2-3} = \frac{-640\text{ft}}{1\text{min}} }\) |
| (3, 640) to (4, 0) |
\(\mathsf{ \frac{\text{rise}}{\text{run}} = \frac{0-640}{3-4} = \frac{-640\text{ft}}{1\text{min}} }\) |
Notice that the slope is always \(\mathsf{ \frac{-640\text{ft}}{1\text{min}} }\).
