You have learned that inequalities are mathematical statements that compare two numbers or quantities that are not equal. The symbols you can use to describe the relationship between the two numbers or quantities that are not equal are reviewed in the table below.
Symbol |
Meaning |
|---|---|
\( \gt \) |
Greater than |
\( \lt \) |
Less than |
\( \geq \) |
Greater than or equal to |
\( \leq \) |
Less than or equal to |
\( \neq \) |
Not equal to |
Question
What do the symbols \( \lt \) and \( \gt \) have in common with each other? What do the symbols \( \geq \) and \( \leq \) have in common with each other?
The inequality symbols \( \lt \) and \( \gt \) represent strict inequalities; whereas, the symbols \( \geq \) and \( \leq \) represent non-strict inequalities.
If an inequality contains a variable, then you can use a number line to create a visual reference to show all the values that make the inequality true. For example:
Use a number line to graph the inequality \( 0 \leq x \).
The steps for graphing inequalities on a number line are shown in the table below. Click each step to see it applied to the example.
This is a non-strict inequality. 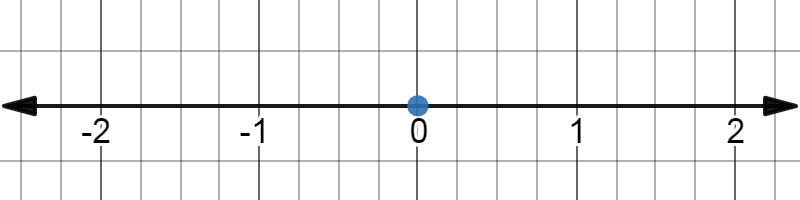
0 plotted on a number line with a closed circle. |
|
The variable is the on the right-hand side of the inequality. 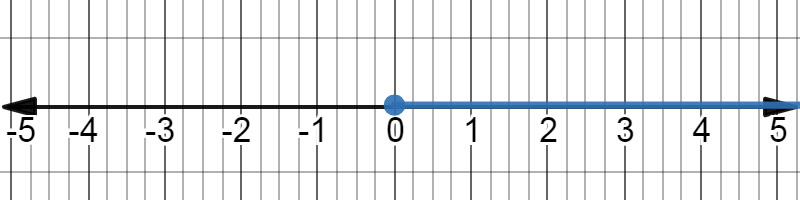
The inequality \( 0 \leq x \) on a number line. |
|
Substitute \( x = 1 \) \( 0 \leq \left( 1 \right) \) \( 0 \leq 1 \) |
How well can you graph inequalities on a number line? Use the activity below to practice. Match the inequality on the left with its graph on the right.
