In a previous lesson, you learned that a nuclear reaction is a reaction that affects the nucleus of an atom. Nuclear power plants use the energy generated from a nuclear reaction that takes place in a vessel called a nuclear reactor. The fuel in the nuclear reactor is made into rods as shown in this video.
In this lesson, you will develop models to show what is happening in each of these nuclear reactions:
-
the nuclear fusion reactions that produce the uranium that is used in nuclear reactors
-
the nuclear fission reactions that take place inside of the uranium that is used in nuclear reactors
-
the radioactive decay reactions that take place inside of uranium and the waste from nuclear reactors
In order to understand why these nuclear reactions occur, it is first necessary to understand the forces present in the nucleus of the atom.
Recall that the nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. Protons are positively charged and will push apart from each other, yet the nucleus stays together. For the nucleus to stay together, there must be a force that holds the protons and neutrons together. This is called the strong nuclear force. The strong nuclear force is an attractive force between protons and neutrons as well as between two neutrons.
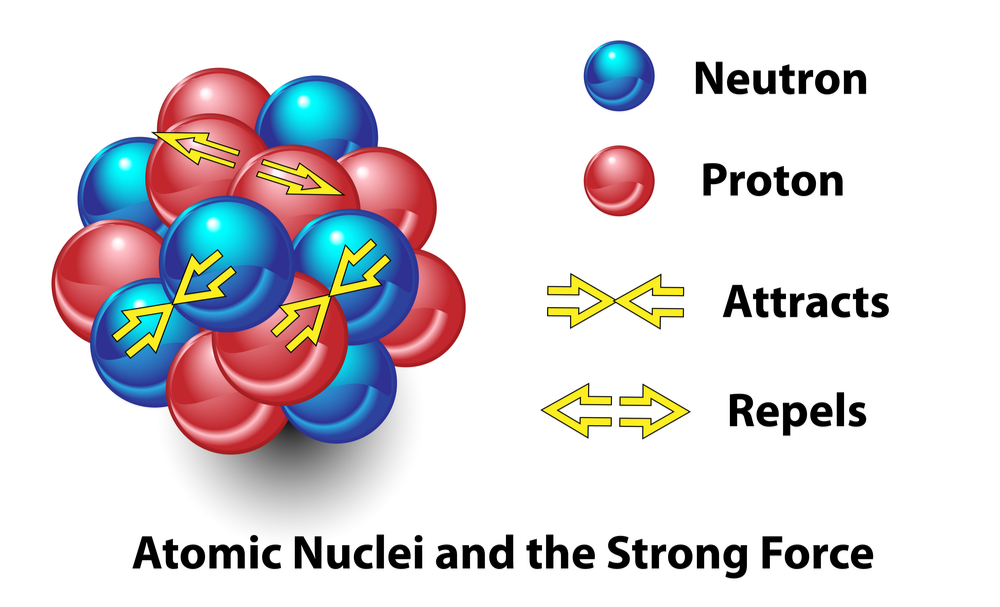
A radioisotope is an isotope of an atom that has an unstable nucleus. A nucleus becomes unstable when the strong nuclear force can no longer overcome the repulsive electric forces among the protons. The energy required to bond the subatomic particles in nuclei together is released during certain nuclear reactions.
Question
The fuel used in a nuclear power plant is an isotope of uranium, U-235. All isotopes of uranium have an atomic number of 92. How many protons and neutrons does this nuclear fuel have?
Uranium has an atomic number of 92, which means that it has 92 protons. The mass of this isotope is 235 u; so, to find the number of neutrons, subtract 92 from 235. Uranium-235 has 143 neutrons.
What is the strong nuclear force? What does this force have to do with the changes that occur during nuclear processes?


