Uranium is radioactive, which means that it has an unstable nucleus. When atoms are unstable, they can become more stable by undergoing radioactive decay. Recall that there are three main types of radioactive decay (shown below). Click each one to learn about it.
An alpha particle has 2 protons and 2 neutrons and is basically a helium nucleus. During alpha decay, an alpha particle is given off from the nucleus of the atom. This decreases the atomic number of the daughter nucleus by 2 and the mass by 4.
Due to the large size of the helium atom and its mass, an alpha particle is very slow moving and does not cause a large amount of damage.

This illustration shows alpha radiation because a helium nucleus is produced, which is an alpha particle.
Beta particles are just high-speed electrons. In beta decay, a beta particle is given off. This comes from a neutron being broken down into a proton and an electron. The proton stays in the nucleus and increases the atomic number by one, and the electron leaves. The mass of this nucleus stays the same.
The beta particle moves faster and can cause more damage than the alpha particle.
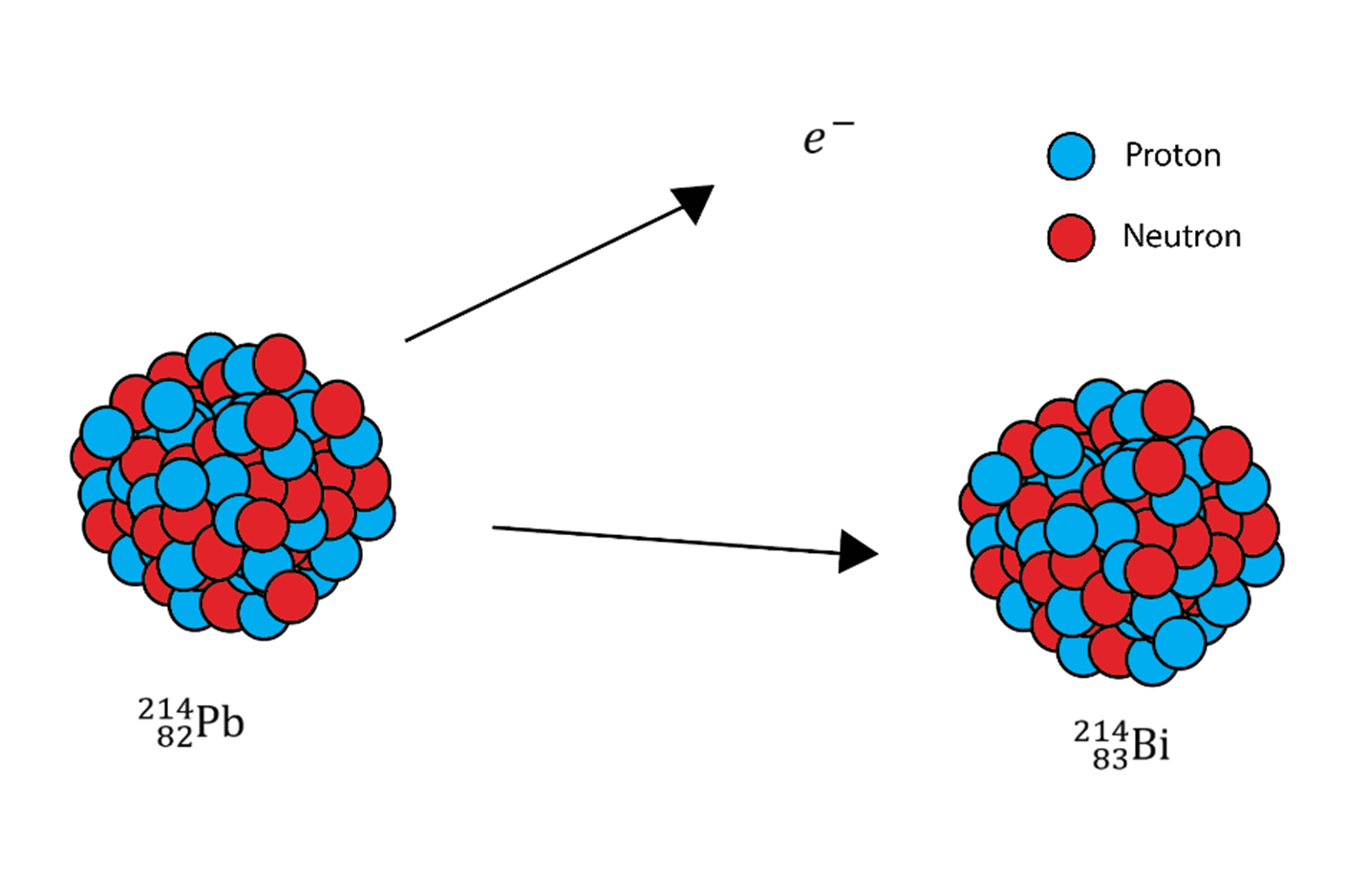
This illustration shows beta radiation because an electron is released, and a neutron is converted into a proton.
A gamma ray is just energy given off from the nucleus of an atom. In gamma decay, a gamma ray is given off. There are no particles given off, so this does not change the atomic number or the mass of the atom; it only changes the energy in the nucleus.
The gamma ray is not a particle; it is a wave and can cause the most damage.
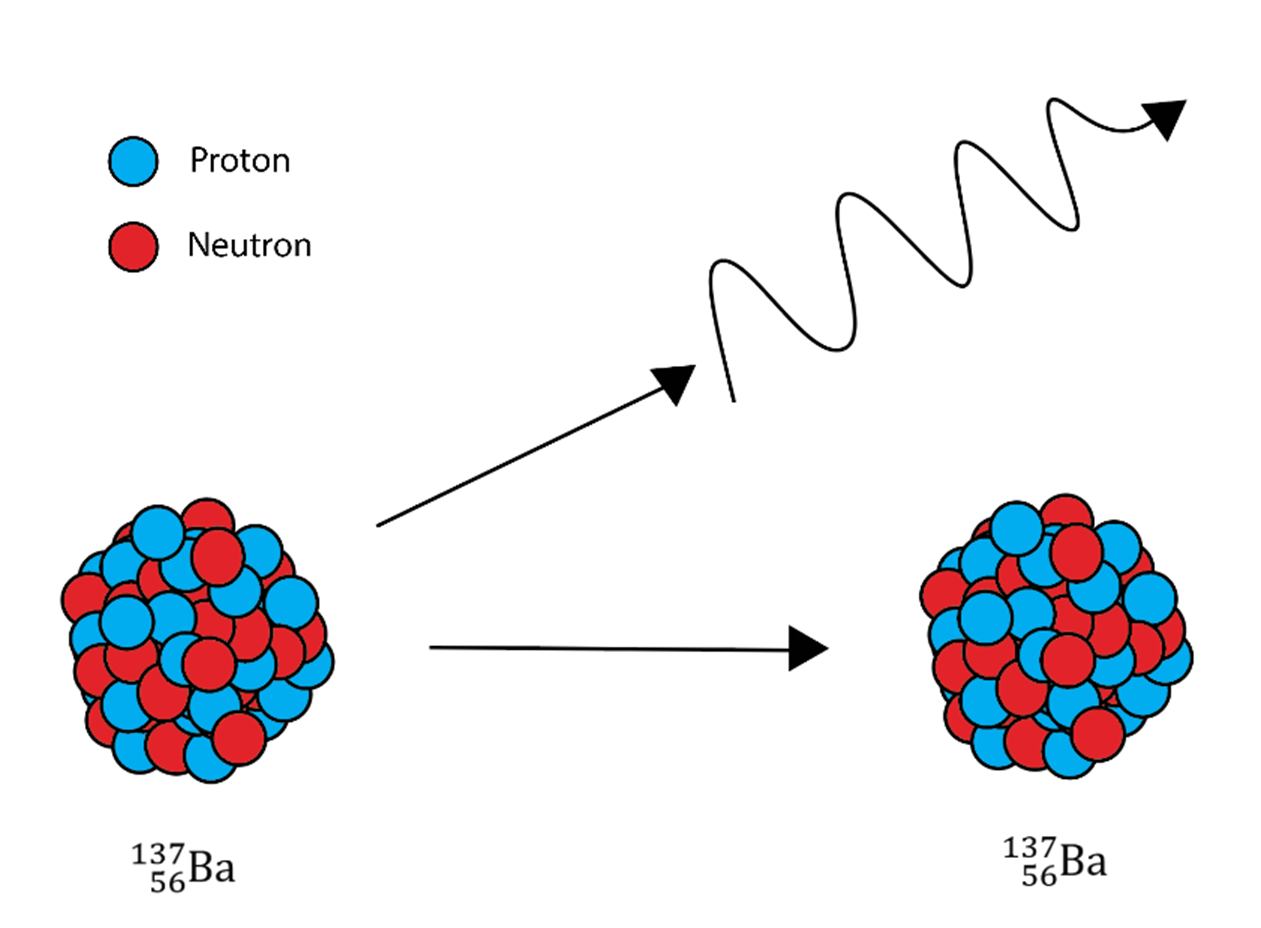
The illustration shows gamma radiation because the nucleus stays the same and only electromagnetic radiation is given off.
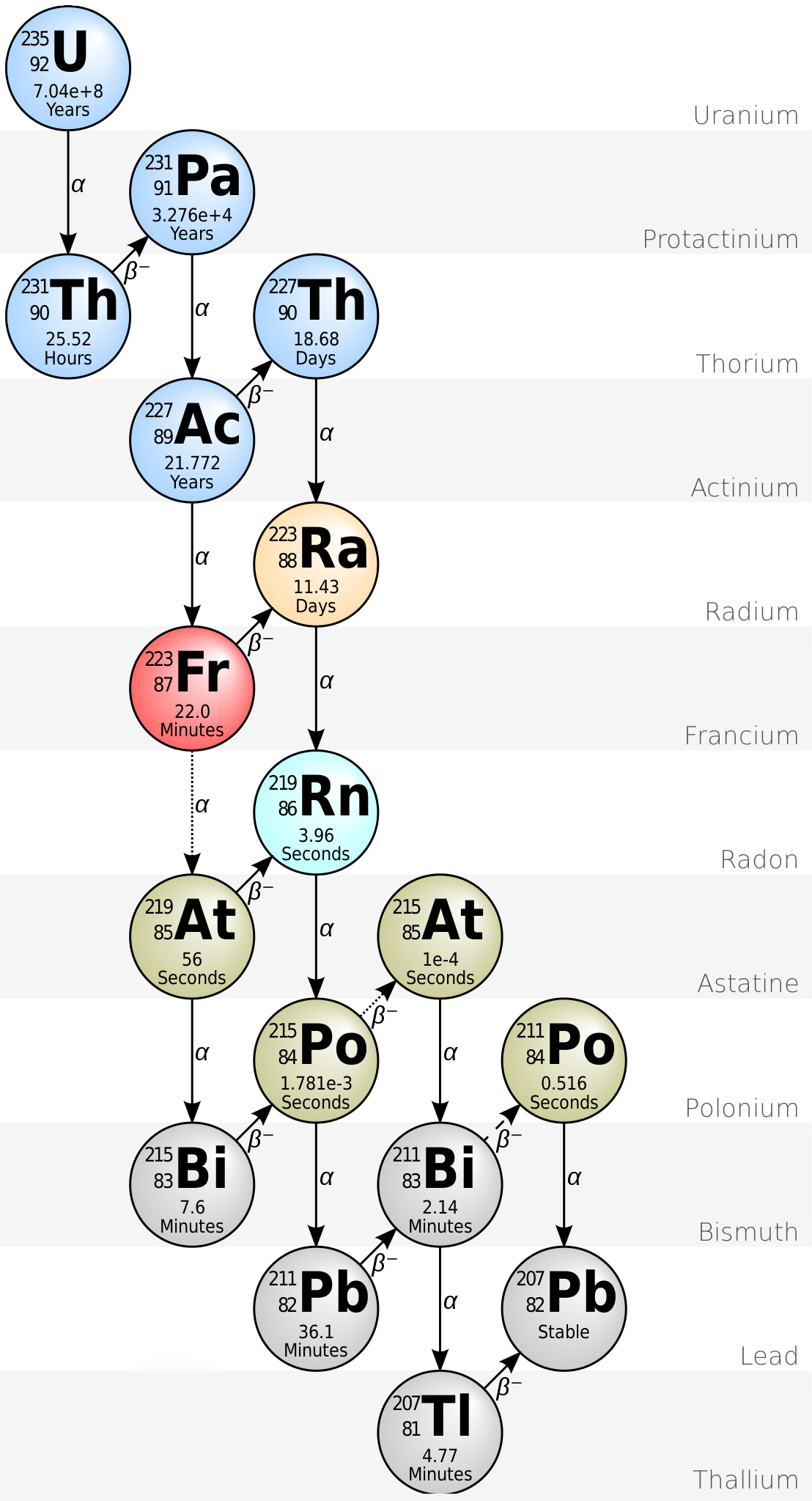
These types of decay are associated with the fuels and wastes of nuclear power plants. However, one nuclear reaction is not always enough to produce a stable isotope. A decay series is a series of radioactive isotopes produced by successive radioactive decay until a stable isotope is reached. The parent nucleus is the heaviest isotope of each decay and the isotopes produced by the decay of the parent are called daughters.
Uranium-235 has a half-life of 703.8 million years. This means that it takes 703.8 million years for one half of its nuclei to decay to its products.
When the uranium used in nuclear power plants decays, it undergoes a number of reactions, each producing either an alpha or a beta particle, until it eventually produces lead-207 which is stable.
The products of the nuclear reactions that take place in nuclear power plants must be stored. The storage of radioactive nuclear waste is a major issue because--for some types of nuclear fuels--the wastes have half-lives that are thousands of years. In order to use nuclear power effectively, methods need to be developed to deal with this waste.
Question
When does a radioactive decay series end?
The decay reactions continue until a stable, nonradioactive isotope is formed.
Explain how each of the three main types of radioactive decay can change the nucleus of an atom and how radioactive decay could be an issue for nuclear power.

