 "Reduce, reuse, recycle"--you've probably seen these words many times before. As stewards of the environment, we try to recycle as much as possible. Recycling involves processes like melting down plastic bottles or metal cans to make new products. In a way, recycling mirrors what happens in an ecosystem. An ecosystem is a group of organisms and the environment in which they live.
"Reduce, reuse, recycle"--you've probably seen these words many times before. As stewards of the environment, we try to recycle as much as possible. Recycling involves processes like melting down plastic bottles or metal cans to make new products. In a way, recycling mirrors what happens in an ecosystem. An ecosystem is a group of organisms and the environment in which they live.
Ecosystems are made of abiotic and biotic factors. Abiotic factors are the nonliving parts of an ecosystem, such as temperature, weather, rocks, soil, and water. Biotic factors are anything in an ecosystem that is alive, like bacteria, fungi, plants, and animals.
All living things require energy. Scientists say that energy "flows" through an ecosystem from primary producers (plants and other organisms that convert light energy into chemical energy) through different types of consumers (organisms that get their energy from other organisms.) Energy enters and leaves an ecosystem. For example, energy often enters an ecosystem as light energy from the sun and is converted to glucose (a sugar) by primary producers.
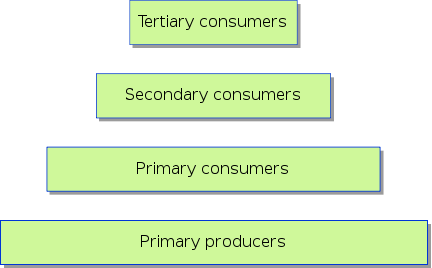
Energy flows in an ecosystem from primary
producers through different types of consumers.
Organisms that make up the biotic part of an ecosystem need energy to survive, but that's not all they need. Certain abiotic factors move through ecosystems in patterns called biogeochemical cycles.
Question
What kinds of abiotic factors do you think the biotic parts of an ecosystem require to survive?
