The hydrologic (water) cycle is the way in which water moves through the ecosystem. Equally as important to life as water is the element carbon, which moves through an ecosystem by the carbon cycle. Carbon is an element that is one of the building blocks of life; that is, it is present as part of many of the molecules that cells use for energy and as part of their structure.
The element carbon, which is present in all living things, moves through an ecosystem by the carbon cycle. Click through the slide show to learn more about how carbon moves through this biogeochemical cycle.
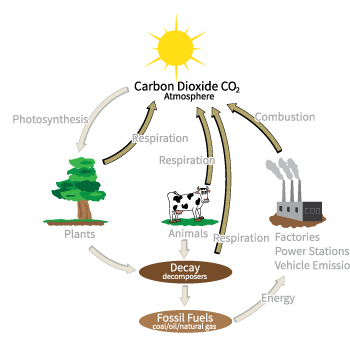
Carbon Dioxide
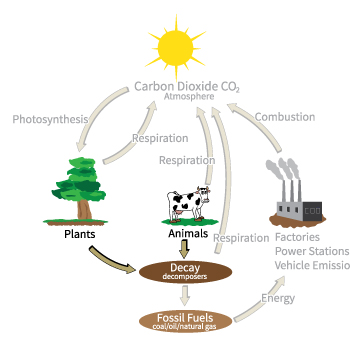
The atmosphere is one of the major reservoirs of carbon in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere in several different ways. Living cells make energy through a process known as cellular respiration. During this process, oxygen and a sugar called glucose are used to make energy, and carbon dioxide is released as a by-product. (You exhale carbon dioxide when you breathe out.) Plants and animals both use cellular respiration, as do some bacteria. Humans also release a lot of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere by the combustion (burning) of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. Photosynthesis
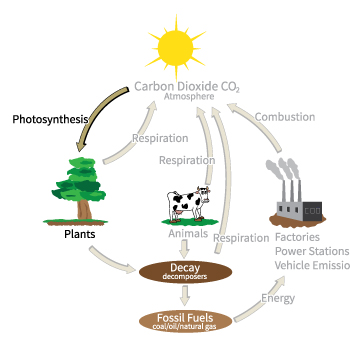
Carbon leaves the atmosphere mostly through photosynthesis, which is the process in which green plants and other organisms take light energy and use it to create chemical energy in the form of the sugar glucose. This is called carbon fixation and is how most carbon enters the earth. Carbon fixation refers to the conversion of carbon dioxide to organic compounds by living organisms. Carbon fixation specifically happens during the step of photosynthesis in which carbon atoms from carbon dioxide become part of the structure of glucose. Decomposition
Carbon enters the lithosphere when organisms called decomposers break down dead plant and animal tissue into its components. Bacteria and fungi are common decomposers. Fossil Fuels
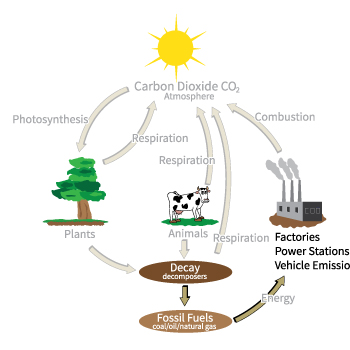
Large amounts of carbon are stored in fossil fuels, such as coal, natural gas, and oil. This is because these fuels originate from the bodies of plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. The carbon from fossil fuels reenters the atmosphere when they are burned by humans through combustion. The Ocean
Although it's not shown in the carbon cycle illustration, the ocean acts as another very large reservoir for carbon. In addition to being present in marine life, carbon dioxide is absorbed by ocean water itself. |
 |
Test your knowledge of the carbon cycle by answering these questions.
Which statement describes how an increase in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has affected ecosystems?
- It has decreased the amount of heat trapped next to the earth's surface.
- It has decreased the amount of photosynthesis that occurs globally.
- It has increased the amount of acid rain.
- It has increased (made more basic) the pH of the oceans.
Carbon dioxide decreases the pH of solutions.
Carbon dioxide decreases the pH of solutions.
Carbon dioxide decreases the pH of solutions.
Carbon dioxide decreases the pH of solutions.
How does most carbon enter living things?
- transpiration
- photosynthesis
- decomposition
- cellular respiration
Carbon is "fixed" during this process.
Carbon is "fixed" during this process.
Carbon is "fixed" during this process.
Carbon is "fixed" during this process.
Which statement describes a way in which carbon enters the atmosphere?
- creating fossil fuels
- photosynthesis
- cellular respiration
- decomposition
All cells need to create energy and use oxygen.
All cells need to create energy and use oxygen.
All cells need to create energy and use oxygen.
All cells need to create energy and use oxygen.
Summary
 Questions answered correctly:
Questions answered correctly:
 Questions answered incorrectly:
Questions answered incorrectly: