 This earthworm is an Annelid, which means it is a segmented worm. Notice how the body is made up of distinguishable ring-like segments.
This earthworm is an Annelid, which means it is a segmented worm. Notice how the body is made up of distinguishable ring-like segments.
Phylum Annelida contains the most complex type of worms--segmented worms. Segmented worms have bodies like a tube within a tube, and the tubes are divided into identical segments, sort of like donuts piled on top of each other. Each segment has organs for a specific task, but all segments contain excretory organs and nerves.
There is fossil evidence of segmented worms from 530 million years ago. About 70 percent (8000 different species) of all annelids live in marine habitats. The other 30 percent (about 3100 different species) live on land. There are three major classes of Annelids--Polychaeta, Oligochaeta, and Hirudinea. Although there are many differences amongst the annelids, they have many common features. In the activity below, click through the tabs to learn about the different features of annelids.
Septa
Setae
Parapodia
Coelom
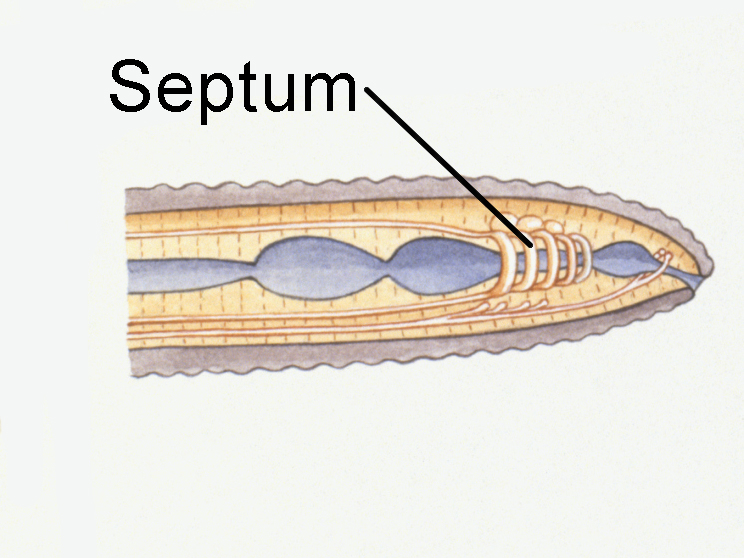
In between each segment is a septum (plural: septa), or a thin dividing wall of tissue. There are openings within each septum for the gut and blood vessels to pass through.

Setae are very thin bristles that line the outer surface of the Annelid, as pictured. These setae act as a type of anchor that helps the Annelid grasp soil when moving. The presence, absence, and amount of setae are important factors in grouping Annelids into their particular classes.
![By Alexander Semenov (originally posted to Flickr as Metallic snake) [CC-BY-2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://s3.amazonaws.com/cms.accelerate-ed.com/image/5b15e59f-e8fa-44f1-8652-f93d8bf8b8f1.jpg)
This predatory Annelid has many feathery parapodia.
Another distinguishing feature of Annelids are parapodia, which are muscular, fleshy appendages that are present in many Annelids. They are specifically designed to help Annelids crawl or swim, for many of them are shaped like paddles. The presence or absence of parapodia is an important factor in grouping Annelids into their particular classes. In addition to parapodia, what other body feature of annelids is involved in grouping them into their classes? Think of the answer, then click Show Me to see if you are correct.

Annelids are grouped into their classes depending on the presence, absence, or amount of setae and the presence or absence of parapodia.
![By Doc. RNDr. Josef Reischig, CSc. (Author's archive) [CC-BY-SA-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://s3.amazonaws.com/cms.accelerate-ed.com/image/26c2eadd-3843-4ca5-8eaa-fe3c51e697e9.jpg)
This is a cross section of an earthworm, in which the coelom is visible.
All Annelids have a coelom, which is a fluid-filled body cavity in which all the organs are suspended and protected by mesoderm. The presence of a coelom indicates a high level of complexity and specialization within an animal. What other animals have you studied that contain a coelom? Think of the answer, then click Show Me to see if you are correct.

Mollusks (i.e. snails, oysters, octopuses) contain a coelom.
In the activity below, match the vocabulary word with its definition.
setae
septa
parapodia
annelid
coelom
|
thin tissue that divides the segments of annelids
muscular, fleshy appendages on some annelids
bristles on the outside of some annelids
fluid-filled cavity surrounded by mesoderm
segmented worm
|
