Both flatworms and roundworms are the simplest of all worms, having no true coelom and the majority having to live on or inside a host for nutrients. Within the Platyhelminthes and Nematoda phyla are some variations amongst the classes. On this page and the next is an overview of the common classes of flatworms and roundworms. In the activity below, click each tab to learn about the different classes of flatworms.
Turbellaria
Cestoda
Trematoda
![By Christopher Laumer [CC-BY-2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://s3.amazonaws.com/cms.accelerate-ed.com/image/573b026e-56ef-42b9-ae53-9262ea3ceae4.jpg)
Class Turbellaria includes the free-living marine flatworms, such as the worm pictured in the image. This class is unique in comparison to other flatworm classes because these flatworms are free-living rather than parasitic. Most other flatworms need a host to survive.
Turbellarians can reproduce asexually and sexually. Turbellarians can reproduce asexually by attaching one end of their body to a hard surface, then stretching their body until they split in two. The two pieces then grow into individual worms.
All Turbellarians are hermaphrodites. During times of sexual reproduction, Turbellarians exchange sperm with each other. Because hermaphrodites have both eggs and sperm, both worms' eggs get fertilized by the other worms' sperm.
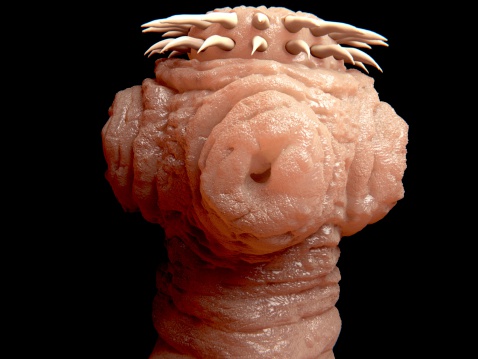
Class Cestoda is composed of the parasitic tapeworms that mostly infect vertebrates. Tapeworms have suckers and hooklike structures on their head, which help them attach to the intestinal wall of their hosts. Cestodes absorb food directly from their host and can grow up to 40 feet long inside of a human's intestines. The tapeworm grows so long because as it obtains nutrients, it adds chains of proglottids--rectangular body parts--to its body for an indefinite period of time.
Young tapeworms grow in the muscles of certain animals. Taenia saginata is a tapeworm found in cow muscle. If a human eats undercooked beef, he may be infected with this harmful parasite. The tapeworm then grows in the human intestinal tract into an adult. When it gets to this point, it is very difficult to treat. This is why it's important to be sure meat is fully cooked before eating it.
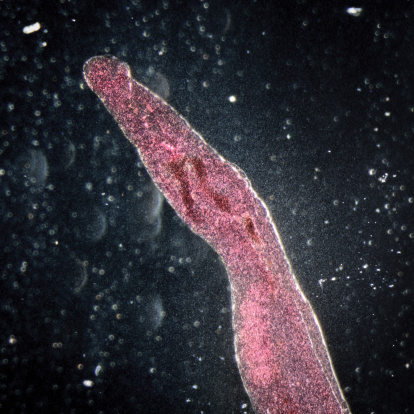
The largest flatworm class includes Trematoda, which consists of parasitic worms called flukes. Like Cestodes, some Trematodes are endoparasites, which means that they are parasites that live inside a host. Some Trematodes are also ectoparasites, which means they can live outside the host. Trematodes have a tegument, which is a thick layer of cells that protects the worm from being digested.
A common Trematode known to infect humans is the liver fluke, Schistosoma schistosomiaisis. The young liver fluke lives in warm tropical waters and infects a human host when a person walks barefooted in the water. The fluke is able to bore its head through the human's skin and travels into the intestines via the blood vessels of the intestinal wall. The fluke gets nutrients from the human, but over time it blocks the intestinal blood vessels, which causes internal bleeding. This all leads to liver damage. Eggs are released in the human feces. If snails get access to the feces, the snail ingests the eggs and the baby fluke develops inside the snail. The snails then release the young flukes into the tropical waters where the whole cycle began.
In the activity below, jot down or say to yourself the answer to each question. Click the question to reveal the correct answer.
| What are the three classes of Platyhelminthes? | Turbellaria, Cestoda, and Trematoda |
| What Platyhelminthes class contains free swimming worms? | Turbellaria |
| What are the rectangular growths that elongate the tapeworm body? | proglottids |
| What Platyhelminthes class contains the tapeworm parasite that infects hosts who have eaten undercooked beef? | Cestoda |
| What is the thick layer of cells that protect trematodes from being digested? | tegument |
| What Platyhelminthes class contains the liver fluke? | Trematoda |
