Clearly, the skeletal system of vertebrates has many important functions. These functions include supporting the animal's body, protecting vital internal organs, creating blood cells, and storing minerals like calcium. But what materials make up the vertebrate skeletal system, and how are these materials put together? Click each tab in the activity below to find out.
Bone vs. Cartilage
Axial vs. Appendicular Skeleton
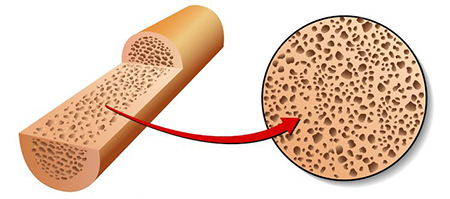 Bone is living connective tissue. |
A skeletal system is made mostly of two materials: bone and cartilage. Bone is, by definition, connective tissue--tissue that provides support or, as its name suggests, connects other tissues. It is porous, meaning it has spaces in it. These spaces give bones flexibility. Bone tissue is alive, and can grow and repair itself, despite being hard due to having minerals, especially calcium. Cartilage is also connective tissue, but it is made of proteins that make it more flexible than bone, and it does not contain the minerals that bones contain.
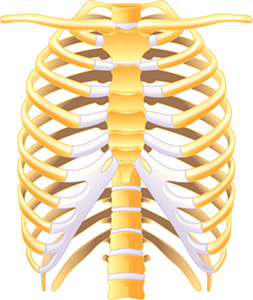 The human rib cage contains both bone (yellow) and cartilage (white). |
 The axial skeleton is made of the skull, spinal column, and rib cage. |
Based on what you recall about the functions of the skeleton, what do you suppose is the main purpose of the axial skeleton? Think about your answer, and then click the Show Me button to see if you are correct.

The primary function of the axial skeleton is protection. The skull protects the brain, the vertebral column protects the spinal cord, and the rib cage protects the heart and lungs.
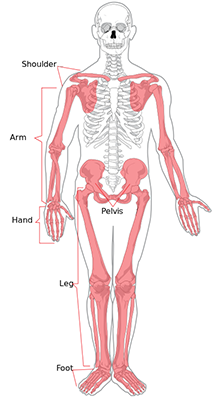 The appendicular skeleton includes the arms and legs. |
Check your understanding of how the vertebrate skeleton is constructed by matching each term to its definition. If you miss any of these items, review the information on this page before moving on.
|
Axial Skeleton
Appendicular Skeleton
Cartilage
Bone
|
more rigid connective tissue found throughout the human skeleton
made of the arm and leg structures
very flexible connective tissue found in ears and nose
made of the rib cage, skull, and spinal column
|
Try again.
