
Cancer occurs when cells in a part of the body begin to grow out of control. Normal cells divide and grow in an orderly fashion, but cancer cells do not. They continue to grow and crowd out normal cells. There are many kinds of cancer, but they all have in common this out-of-control growth of cells. A tumor is a mass of abnormal cells. Tumors can be benign, or non-cancerous. Tumors that are malignant, or cancerous, often spread to other parts of the body. Different kinds of cancers can behave very differently.
What causes cancer?
Treating Cancer
Warning Signs for Cancer

According to the American Cancer Society, smoking accounts for about 30% of all cancer deaths in the United States, including about 80% of all lung cancer deaths. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in both men and women, and is one of the hardest cancers to treat.
In addition, more than five million cases of skin cancer were diagnosed in the United States in 2012, making skin cancer the most common cancer. All types of skin cancer are due to exposure to the sun.

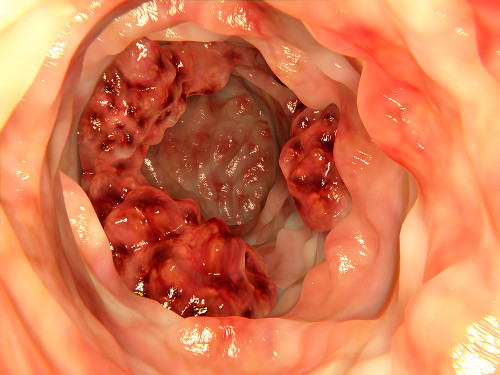
More than one million people in the United States are living with colon cancer. More than 50,000 deaths from this disease are expected in 2017. Colon cancer is related to diets that are low in fiber and high in fat.
You can lower your cancer risk by avoiding tobacco, protecting yourself from the sun, and eating low-fat, high-fiber foods.

Cancer treatment is based on the kind of cancer and what stage it is in. Many different treatments for cancer have been developed; and today, over half of the people who get cancer are cured. The three main methods of treatment are surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
When cancer is treated surgically, tumors are removed and damaged organs are repaired. Radiation uses X-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy destroys cancer cells with powerful drugs. Chemotherapy is used to fight cancer that has spread to numerous parts of the body.
People who notice one of these seven warning signs should see a doctor right away.
- Change in bowel or bladder habits
- A sore that does not heal
- Unusual bleeding or discharge
- Thickening or lump in the breast or elsewhere
- Indigestion or difficulty swallowing
- Obvious change in a wart or mole
- Nagging cough or hoarseness
