There are four different scenarios that effect the apparent weight of an object: when the apparent weight is greater than actual weight, when the apparent weight is less than the actual weight, when the apparent weight is equal to the actual weight, and when the apparent weight is zero. Use your knowledge of apparent weight and the forces on the object to find the solution to each problem below.
| Problem | Picture | Given/Find | Equation | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
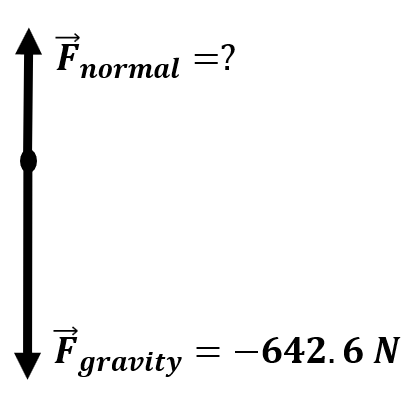
| A 65.5 kg man stands on a scale in an elevator. During its initial decent, the elevator speeds up at a rate of -4.12 m/s2. What the scale read during the initial decent? |
|
\(\small\mathsf{ m = 65.5 \text{ kg} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \overrightarrow{a} = -4.12 \text{ m/s}^2 }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \overrightarrow{F}_{weight} = -642.555 \text{ N} }\) |
\(\small\mathsf{ F_{net} = m \overrightarrow{a} = \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} + \overrightarrow{F}_{weight} }\) | \(\small\mathsf{ (65.5 \text{ kg})(-4.12 \text{ m/s}^2) = \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} + -642.555 \text{ N} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ -269.86 \text{ N} = \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} + -642.555 \text{ N} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} = 373 \text{ N} }\) |
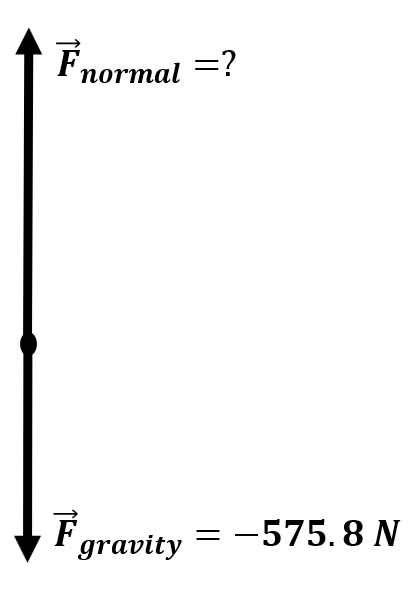
| A 58.7 kg woman stands on a scale in an elevator. The elevator accelerates upward at a rate of 2.87 m/s2 as it moves from the bottom floor to the second floor. During the period of acceleration, what does the scale read? |
|
\(\small\mathsf{ m = 58.7 \text{ kg} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \overrightarrow{a} = +2.87 \text{ m/s}^2 }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \overrightarrow{F}_{weight} = -575.847 \text{ N} }\) |
\(\small\mathsf{ F_{net} = m \overrightarrow{a} = \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} + \overrightarrow{F}_{weight} }\) | \(\small\mathsf{ (58.7 \text{ kg})(+2.87 \text{ m/s}^2) = \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} + -575.847 \text{ N} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ 168.469 \text{ N} = \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} + -575.847 \text{ N} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} = 744 \text{ N} }\) |
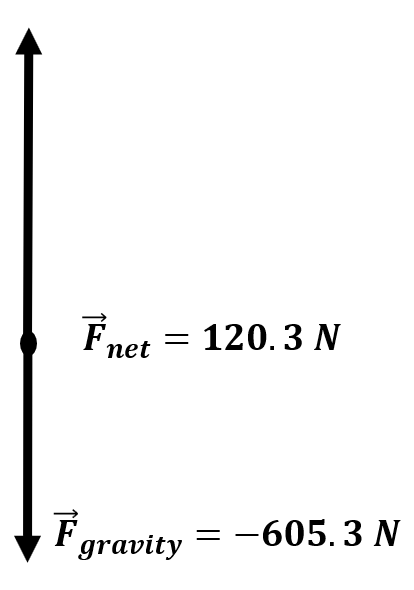
| The net force acting on a 61.7 kg man standing on a scale in an elevator is 120.3 N. What does the scale read? What is the acceleration? |
|
\(\small\mathsf{ m = 61.7 \text{ kg} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \overrightarrow{a} = ? \text{ m/s}^2 }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \ \overrightarrow{F}_{weight} = -605.277 \text{ N} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \ \overrightarrow{F}_{net} = 120.3 \text{ N} }\) |
\(\small\mathsf{ F_{net} = m \overrightarrow{a} = \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} + \overrightarrow{F}_{weight} }\) | \(\small\mathsf{ 120.3 \text{ N} = \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} + -605.277 \text{ N} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} = 726 \text{ N} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ 120.3 \text{ N} = (61.7 \text{ kg}) \overrightarrow{a} }\) \(\small\mathsf{\overrightarrow{a} = \frac{120.3 \text{ N}}{61.7 \text{ kg}} = 1.95 \text{ m/s}^2 }\) |
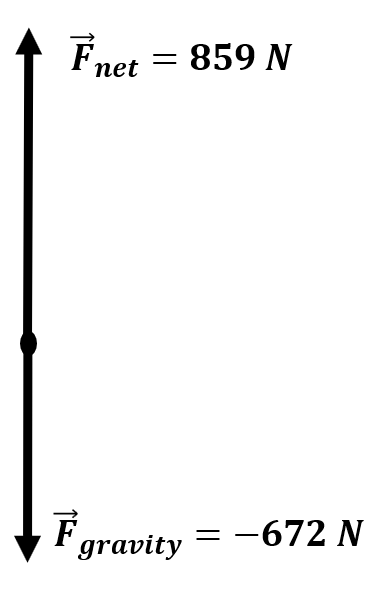
| A man with an actual weight of 672 N stands on a scale in an elevator. His apparent weight during the final "slowing down" of the elevator is 859 N. What is the acceleration? Is the elevator going up or down? |
|
\(\small\mathsf{ m = 68.5 \text{ kg} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \overrightarrow{a} = ? \text{ m/s}^2 }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \overrightarrow{F}_{weight} = -672 \text{ N} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} = 859 \text{ N} }\) |
\(\small\mathsf{ F_{net} = m \overrightarrow{a} = \overrightarrow{F}_{normal} + \overrightarrow{F}_{weight} }\) | \(\small\mathsf{ F_{net} = 859 + -672 \text{ N} =187 \text{ N} }\) \(\small\mathsf{ 187 \text{ N} = (68.5 \text{ kg}) \overrightarrow{a} }\) \(\small\mathsf{\overrightarrow{a} = \frac{187 \text{ N}}{68.5 \text{ kg}} = 2.73 \text{ m/s}^2 }\) The man is going down. The acceleration is positive; thus the elevator must be slowing down in a negative direction. |