So far, we have looked at two factors that can affect the rate of a reaction: the temperature and the concentration of reactants. There are two other factors that can affect the rate of a reaction. Examine each of them in these tabs.
Breaking a reactant into smaller pieces increases its surface area. A greater surface area allows more collisions to occur.
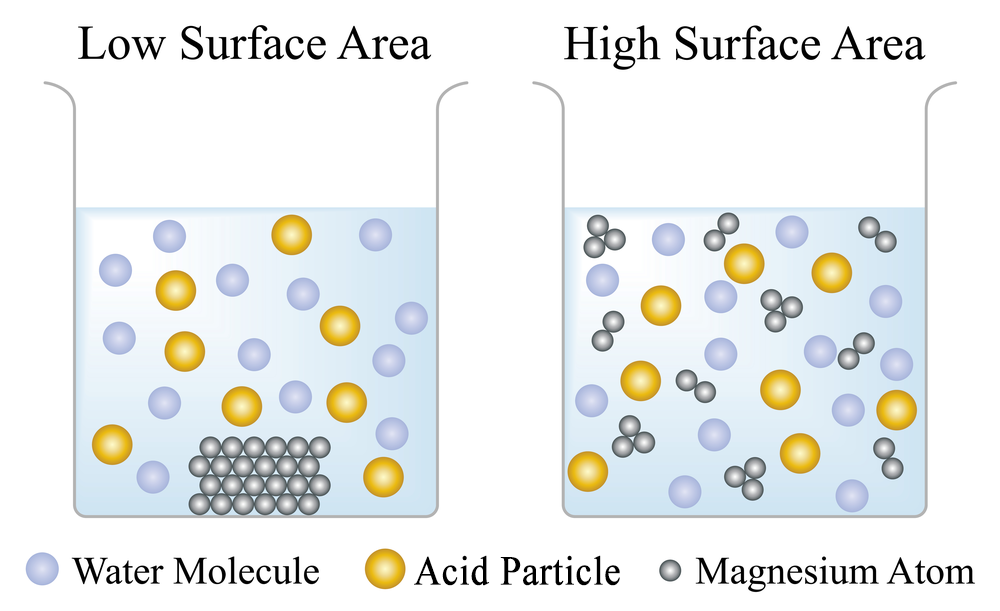
This image shows magnesium reacting with an acid. When the magnesium is in one piece, its surface area is lower, and it does not collide as often with the acid molecules. This means that the reaction rate will be lower. When the magnesium is cut up into smaller pieces, there is more surface area of magnesium to react with acid molecules, and the reaction rate will be higher.
Another way to increase reaction rate is to provide a catalyst. The job of a catalyst is to lower the activation energy needed to start a reaction.
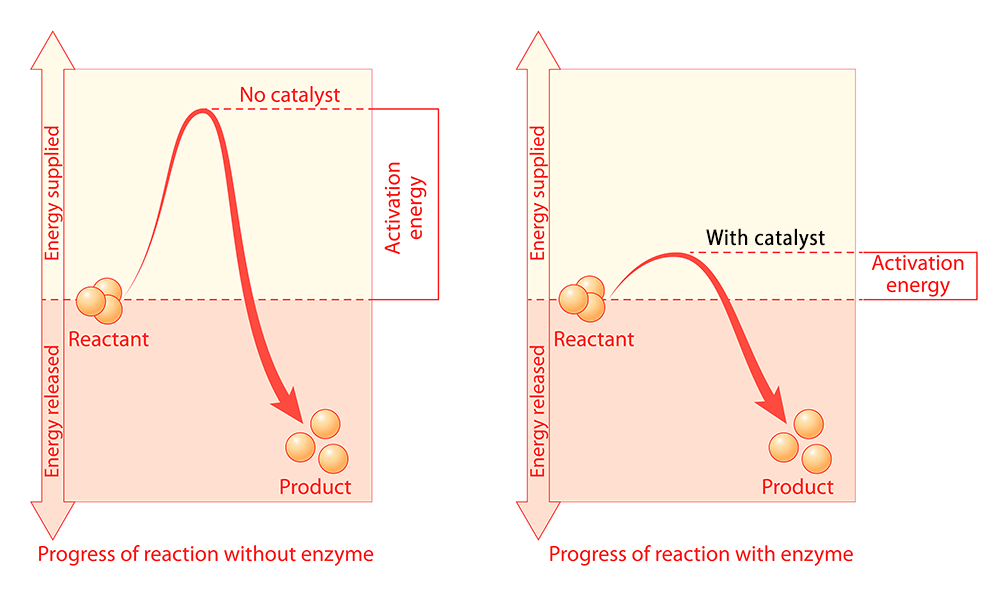
The image on the left shows the activation energy needed to start a reaction without a catalyst. The image on the right shows the activation energy needed to start the same reaction with a catalyst. The catalyst allows the reaction to begin with much less added energy.
What does a catalyst do to the heat required for a reaction to occur?
The heat required would be lower. The molecules do not have to be moving as fast since they do not need to have as much kinetic energy.
Question
How does collision theory explain the effect that surface area and a catalyst have on the rate of a reaction?
The higher the surface area of a reactant, the more possibility there is for reactions, thus increasing the rate of a reaction. The lower activation energy for the catalyzed reaction means that more collisions have sufficient energy to start the reaction.
What type of magnesium (size of particles) is present in the MRE heater? How would this affect the reaction?
The main reaction in the MRE heater is between magnesium and water. Salt and iron are also included in the mixture. What role would these two chemicals play and how do they affect the rate of the reaction?