In an earlier lesson, you learned that the collision theory explains the conditions that are necessary for successful molecular collisions that will result in reactants becoming products. The collision theory states that particles such as atoms and molecules must collide in order to react. The number of collisions between reactant molecules is proportional to the rate of the chemical reaction. The more often the reactant molecules collide, the more often they react, and the faster the reaction rate is.
According to the collision theory, in order for particles such as atoms and molecules to react, they must collide with enough energy and with the proper orientation. This theory explains why reactions occur and how the rates of reactions can be modified. Two of the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction are shown on the tabs below. Read each one to learn how it can be used to modify the rate of a chemical reaction.
There is a certain amount of energy that collisions between reactants must have for a reaction to occur. To increase the rate of a reaction, this energy needs to be increased. To learn how this energy can be increased, we need to understand kinetic energy. Kinetic energy is the type of energy that molecules have when they are moving. This kinetic energy must be enough to break the bonds holding the molecules together. To increase the rate of the reaction, the kinetic energy would need to increase.
One way to speed up the molecules and thus increase their kinetic energy is to heat up the molecules. When heat is added, the molecules will move faster; and faster molecules have more kinetic energy.
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a substance; so, the higher the temperature, the faster the molecules are moving and the more likely the energy from the collisions will be equal to or greater than the activation energy needed.

Low temperature illustration of particles with one collision, increase temperature arrow, and high temperature illustration of particles with 3 collisions.
Earlier in the lesson, you were introduced to the reaction between magnesium and water.
What happened when magnesium was in cold water? Explain.
There was no noticeable reaction. After a period of time, bubbles may form on the magnesium, but it is a very slow process.
A very slow reaction happens because there is not enough energy for the reaction to occur when the water and the magnesium collide. Over time a few reactions may have enough energy to react, but not many.
What happened when magnesium was in hot water? Explain.
As the water was heated, the reaction occurred more quickly. More bubbles formed on the magnesium, showing that hydrogen was produced. Also, an indicator was used to show that one of the products (magnesium hydroxide) was formed.
As the temperature increased, the molecules started moving faster and faster, and more of them had enough energy to react.
Concentration is the amount of a substance in a certain volume. If the concentration of a reactant increases, then there are more of the reactants and more collisions can occur.
If the collisions that are occurring have enough energy, but the reaction is still not occurring quickly, another way to increase the rate of a reaction is to increase the concentration of reactants.
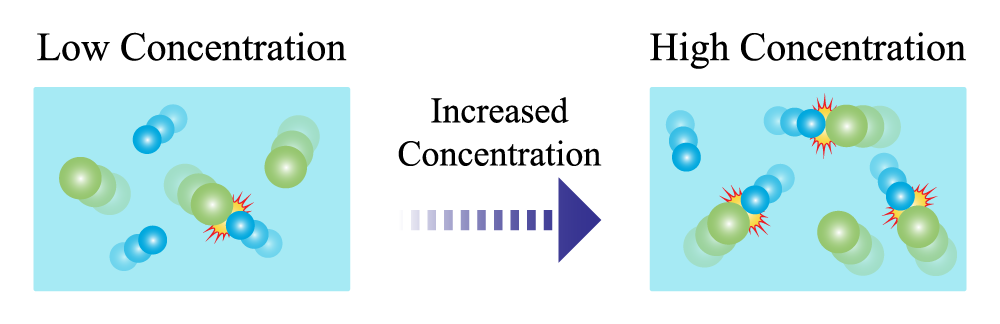
Low concentration illustration of particles with one collision, increase concentration arrow, and high concentration illustration of particles with 3 collisions.
Question
According to collision theory, what must happen in order for a reaction to occur between two molecules?
The two molecules must collide with enough energy and with the proper orientation.
Question
Temperature and concentration are two factors that can affect the rate of a reaction. The rate of a reaction will increase if the temperature is increased. The rate of reaction will also increase if the concentration of one or more of the reactants is increased. What could be done to decrease the rate of a reaction?
If increasing temperature increases the reaction rate, then decreasing temperature will decrease the rate of the reaction. If increasing concentration increases the rate of a reaction, then decreasing the concentration of reactants will decrease the rate of a reaction.
If you wanted to increase the rate at which the MRE heater worked, what could be done to increase the reaction?

