Practice writing electron configurations by completing the activity below. Answer the question on each tab, then check your answer.
Important Reminder
Consult the periodic table to determine the atomic number of each element, which is also equal to its number of electrons.
If you need a periodic table, click below to open an interactive periodic table or to download a PDF.
Write the electron configuration for Carbon (C).
1s2 2s2 2p2.
The shorthand electron configuration is
[He] 2s2 2p2.
If you need help arriving at this answer, click the Solution button.
There is more than one way to arrive at a correct electron configuration. One way is shown here.
| Step 1: Use the box diagram to fill in the electrons for each energy level and orbital. |
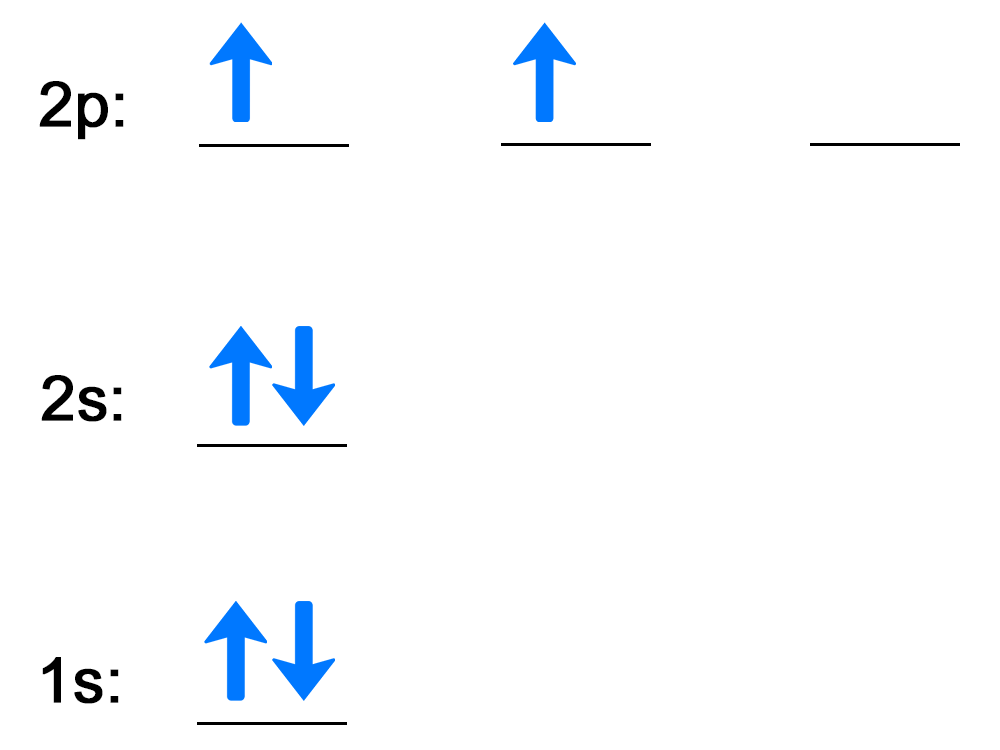
Orbital diagram that uses lines to represent atomic orbitals and arrows to represent electron filling. The diagram has the following attributes from bottom to top:
|
| Step 2: Write out each energy level with the number of electrons as a superscript. |
The first energy level is 1s followed by the two electrons as a superscript behind the s, 1s2. When all energy levels and superscripts are written, the electron configuration for carbon is 1s2 2s2 2p2. There is a superscript of 2 for 2p because there are two electrons in the 2p energy level in the box diagram. |
Write the electron configuration for Nickel (Ni).
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8.
The shorthand electron configuration is
[Ar] 4s23d8.
If you need help arriving at this answer, click the Solution button.
There is more than one way to arrive at a correct electron configuration. One way is shown here.
| Step 1: Use the box diagram to fill in the electrons for each energy level and orbital. |
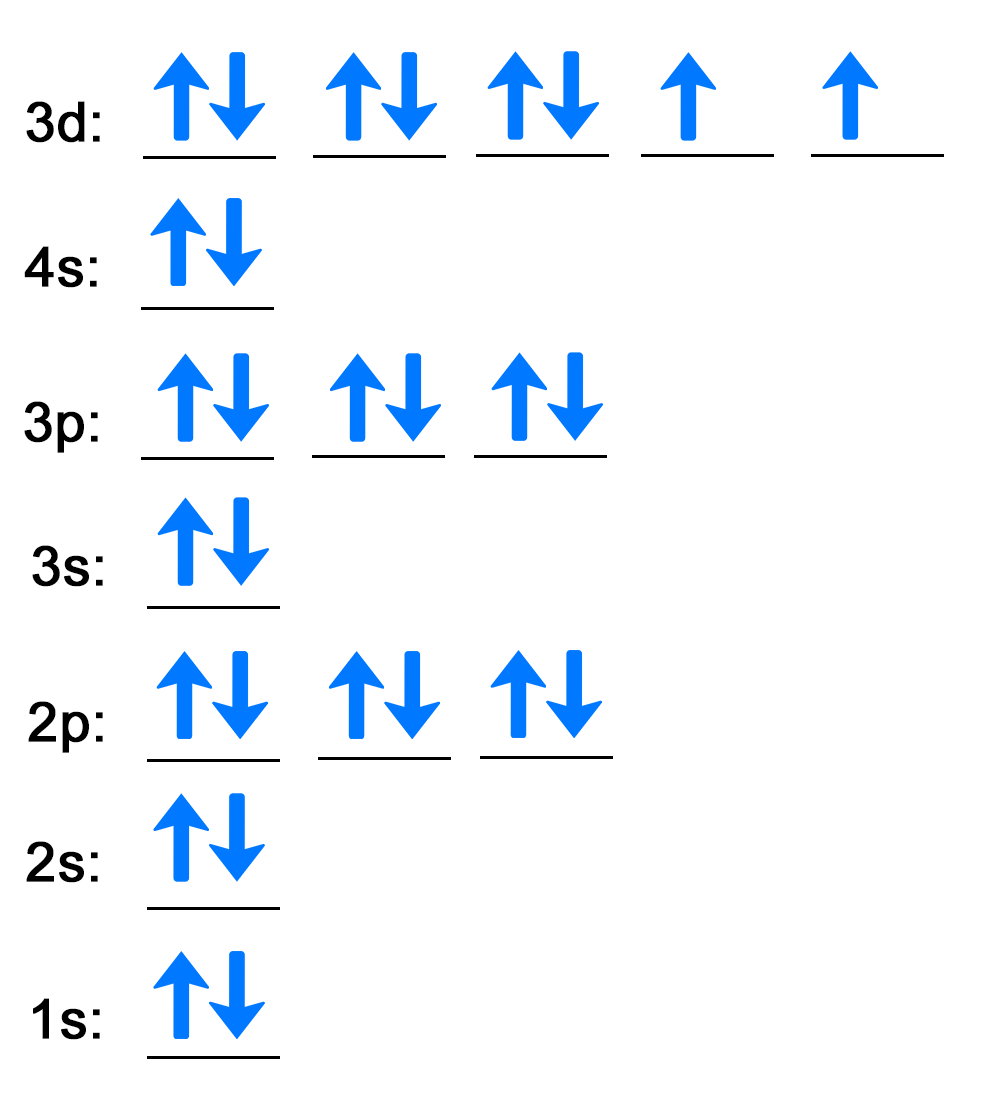
Orbital diagram that uses lines to represent atomic orbitals and arrows to represent electron filling. The diagram has the following attributes from bottom to top:
|
| Step 2: Write out each energy level with the number of electrons as a superscript. |
The first energy level is 1s followed by the two electrons as a superscript behind the s, 1s2. When all energy levels and superscripts are written, the electron configuration for nickel is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8. There is a superscript of 8 for 3d because there are eight electrons in the 3d energy level in the box diagram. |
Note that the 4s energy level is written before 3d according to the orbital-filling chart. This is shown in the periodic table.

Periodic table colored by block. Block S is orange, and includes column 1,2 and Helium. The first row has these notations from top to bottom: 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s, 5s, 6s, 7s. Block d is light orange, and includes columns 3 - 12, and the first column includes this notation from top to bottom: 3d, 4d, 5d, 6d. Block p is yellow and includes column 13 - 18, excluding helium. The first columns blocks contain this notation: 2p, 3p, 4p, 5p, 6p. Block f is green and includes the two rows separated at the bottom of the table. The left column has the notation 4f and 5f from top to bottom.
The first row of d-block is not 4d, but 3d. And by reading across the periodic table from left to right, the 4s block is read before the 3d block. This order is because the energy level for 4s is lower than the 3d energy level. And based on Aufbau's principle, the lowest energy level is filled before moving to the next energy level.
Write the electron configuration for Krypton (Kr).
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6.
The shorthand electron configuration is
[Ar] 4s23d10 4p6.
If you need help arriving at this answer, click the Solution button.
There is more than one way to arrive at a correct electron configuration. One way is shown here.
| Step 1: Use the box diagram to fill in the electrons for each energy level and orbital. |
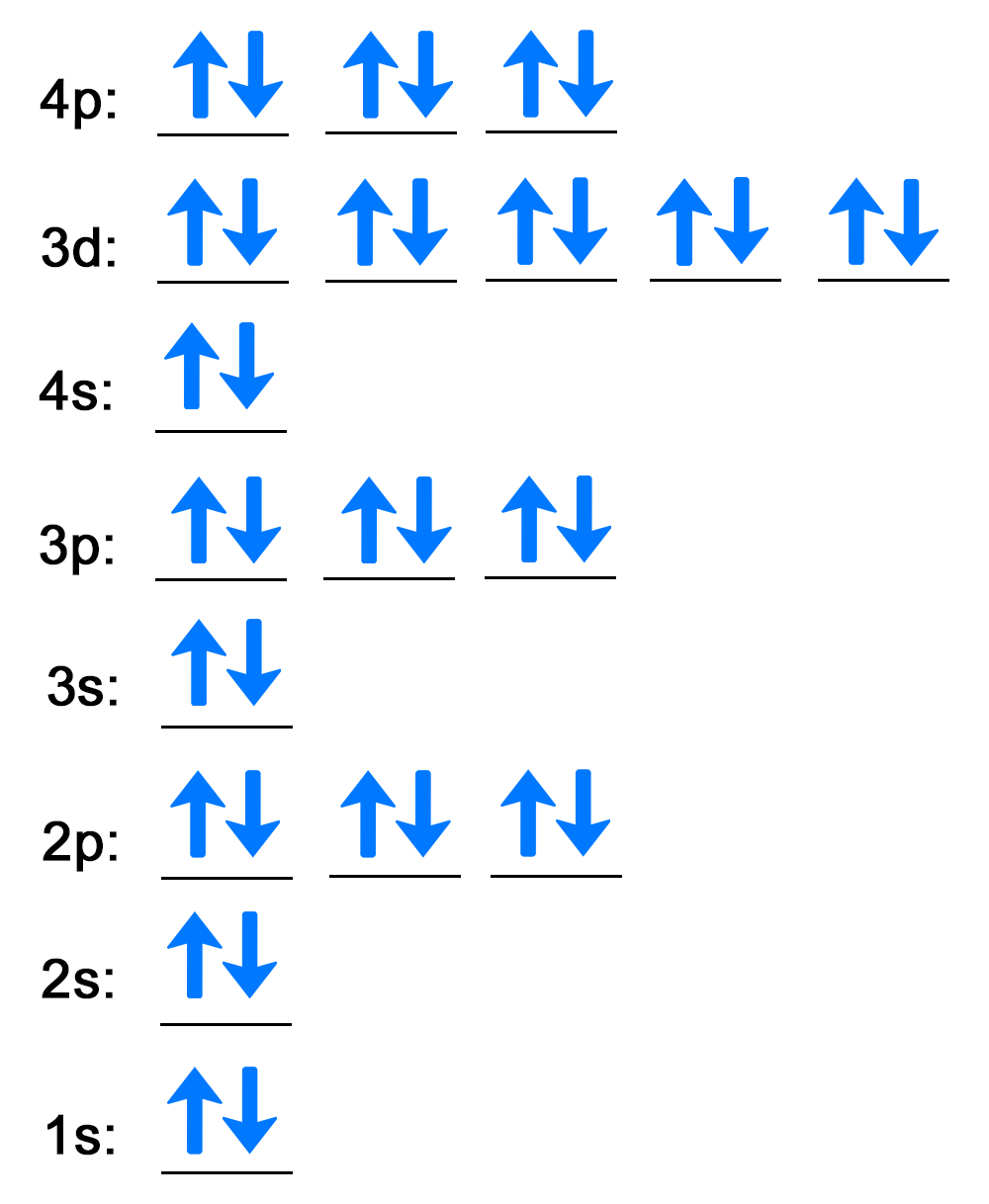
Orbital diagram that uses lines to represent atomic orbitals and arrows to represent electron filling. The diagram has the following attributes from bottom to top:
|
| Step 2: Write out each energy level with the number of electrons as a superscript. |
The first energy level is 1s followed by the two electrons as a superscript behind the s, 1s2. When all energy levels and superscripts are written, the electron configuration for krypton is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6. |
Again, note that the 4s energy level is written before 3d according to the orbital-filling chart. This is shown in the periodic table.

Periodic table colored by block. Block S is orange, and includes column 1,2 and Helium. The first row has these notations from top to bottom: 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s, 5s, 6s, 7s. Block d is light orange, and includes columns 3 - 12, and the first column includes this notation from top to bottom: 3d, 4d, 5d, 6d. Block p is yellow and includes column 13 - 18, excluding helium. The first columns blocks contain this notation: 2p, 3p, 4p, 5p, 6p. Block f is green and includes the two rows separated at the bottom of the table. The left column has the notation 4f and 5f from top to bottom.
The first row of d-block is not 4d, but 3d. And by reading across the periodic table from left to right, the 4s block is read before the 3d block. This order is because the energy level for 4s is lower than the 3d energy level. And based on Aufbau's principle, the lowest energy level is filled before moving to the next energy level.
What is the element that has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4?
sulfur
If you need help arriving at this answer, click the Solution button.
There is more than one way to determine which element has this electron configuration. One way is to use the periodic table of elements to locate each of the blocks.

Periodic table colored by block. Block S is orange, and includes column 1,2 and Helium. The first row has these notations from top to bottom: 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s, 5s, 6s, 7s. Block d is light orange, and includes columns 3 - 12, and the first column includes this notation from top to bottom: 3d, 4d, 5d, 6d. Block p is yellow and includes column 13 - 18, excluding helium. The first columns blocks contain this notation: 2p, 3p, 4p, 5p, 6p. Block f is green and includes the two rows separated at the bottom of the table. The left column has the notation 4f and 5f from top to bottom.
Notice that the last energy level for this electron configuration is 3s2 and 3p4. Since 3s2 is full, find 3p in the periodic table and count 4 elements from left to right. The 4th element is sulfur.
What is the element that has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1?
potassium
If you need help arriving at this answer, click the Solution button.
There is more than one way to determine which element has this electron configuration. One way is to use the periodic table of elements to locate each of the blocks.

Periodic table colored by block. Block S is orange, and includes column 1,2 and Helium. The first row has these notations from top to bottom: 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s, 5s, 6s, 7s. Block d is light orange, and includes columns 3 - 12, and the first column includes this notation from top to bottom: 3d, 4d, 5d, 6d. Block p is yellow and includes column 13 - 18, excluding helium. The first columns blocks contain this notation: 2p, 3p, 4p, 5p, 6p. Block f is green and includes the two rows separated at the bottom of the table. The left column has the notation 4f and 5f from top to bottom.
Notice that the last energy level for this electron configuration is 4s1. Find 4s in the periodic table and count 1 element from left to right. The 1st element is potassium.
