Let’s Learn!
What are multiplication strategies?
Goal:
Goal:

Think About It!
Goal: Use multiplication strategies to solve multiplication sentences.
There are 7 penguins at the zoo. Each penguin laid 8 eggs. How many eggs did the penguins lay in total?
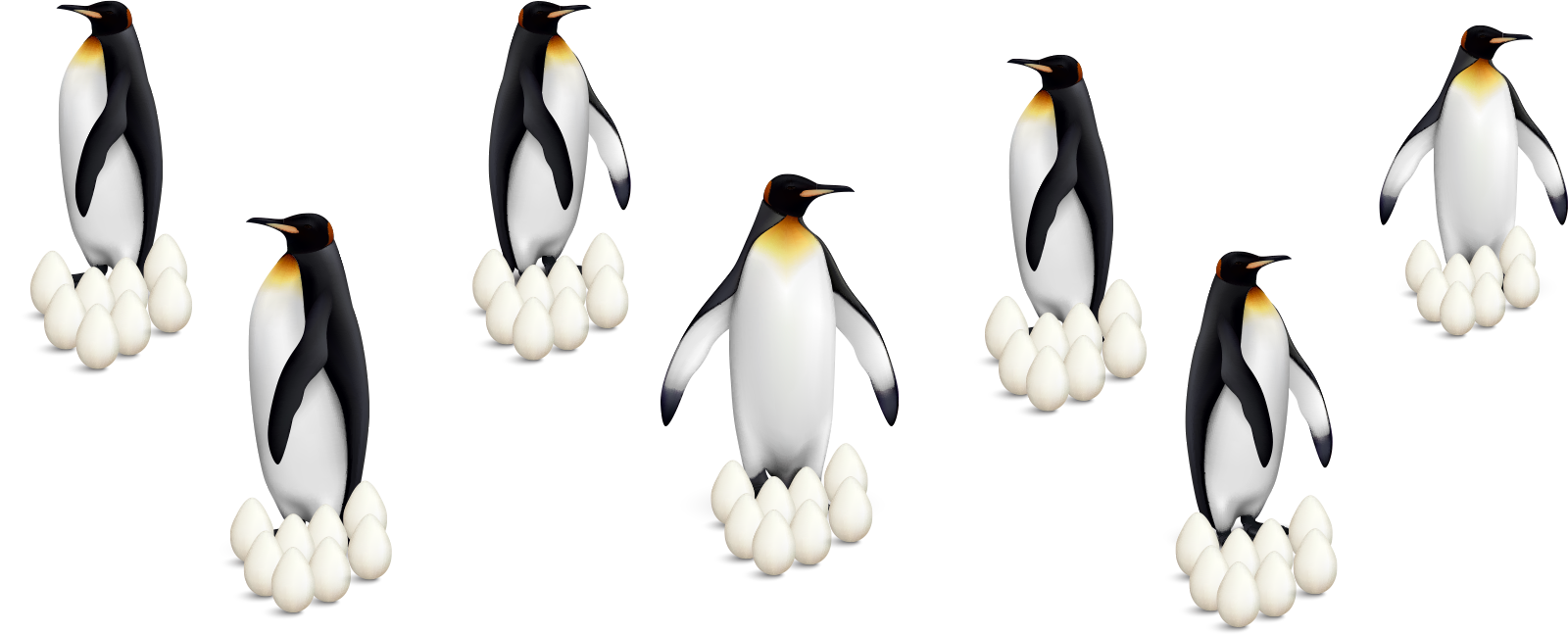

Let’s multiply 7 \({ \times }\) 8 to find out! 7 \({ \times }\) 8 can be written horizontally or vertically. Click “Horizonal” and “Vertical” to see the equations written differently.
Horizontal
7 \({ \times }\) 8 = ?
Vertical
| 7 | |
| \({ \times }\) | 8 |
| ? |
It is time to multiply! Click each tab to review the different ways we can multiply 7 \({ \times }\) 8.
Repeated addition is adding the same number over and over again. This strategy can help us multiply 7 \({ \times }\) 8.
The first factor is the number of times we add. The second factor is the number we add. The sum is also the product of the multiplication sentence.
| 7 | |
| \({ \times }\) | 8 |
| ? |
Can you use this addition sentence to find the product of 7 \({ \times }\) 8? Click the blanks to check your work.
___ + ___ + ___ + ___ + ___ + ___ + ___ = ___
8 + 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 = 56
Nice work! 7 \({ \times }\) 8 = 56 because we added 8 seven times and got 56.
Skip-counting is counting up or back by the same number. This strategy can also help us multiply 7 \({ \times }\) 8.
The number of times we skip count is the first factor. The number we skip count by is the second factor. The answer is the last number in the skip-counting sequence, as well as the product of the multiplication sentence.
7 \({ \times }\) 8 = ?
Can you use this empty skip-counting sequence to multiply 7 \({ \times }\) 8? Click the blanks to check your work.
____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, ____
8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56
You did it! 7 \({ \times }\) 8 = 56 because we skip counted by 8 seven times. The 7th number in the sequence is 56.
A number line is a straight line with arrows at both ends and numbers equally spaced out. Number lines can help us skip count to multiply.
The number of jumps is the first factor. The number of spaces we jump is the second factor. The product is the number the last jump lands on.
| 7 | |
| \({ \times }\) | 8 |
| ? |
This number line jumps in intervals of 8. Use it to multiply 7 \({ \times }\) 8 and click the number line to check your work.
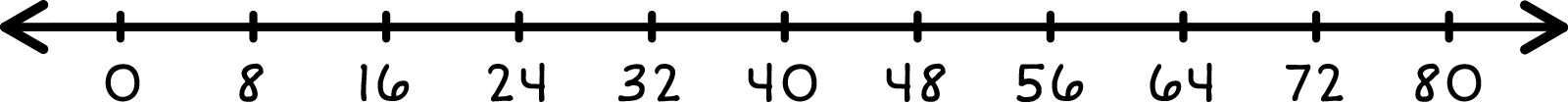

Hooray! The last jump lands on 56, so 7 \({ \times }\) 8 = 56.
An array is a picture that puts an equal number of objects in rows and columns to represent multiplication. The number of rows is the first factor. The number of shapes in each row (the number of columns) is the second factor. The product is the total number of objects in the array.
7 \({ \times }\) 8 = ?
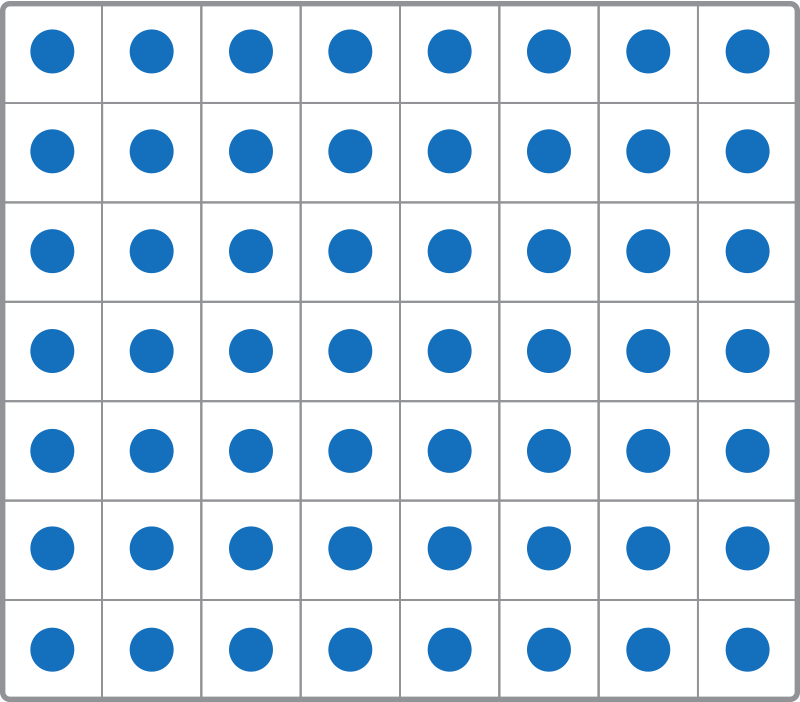

What is 7 \({ \times }\) 8? Use this array to help you find the product.
7 \({ \times }\) 8 = 56
Well done! There are 56 circles in this array, so 7 \({ \times }\) 8 = 56.
A multiplication picture is a picture we can draw to help us multiply. The first factor is the number of circles. The second factor is the number of objects in each circle. The product is the total number of objects in the circles.
7 \({ \times }\) 8 = ?
Can you use these empty circles as part of a multiplication picture to multiply 7 \({ \times }\) 8? Click the circles to check your work.

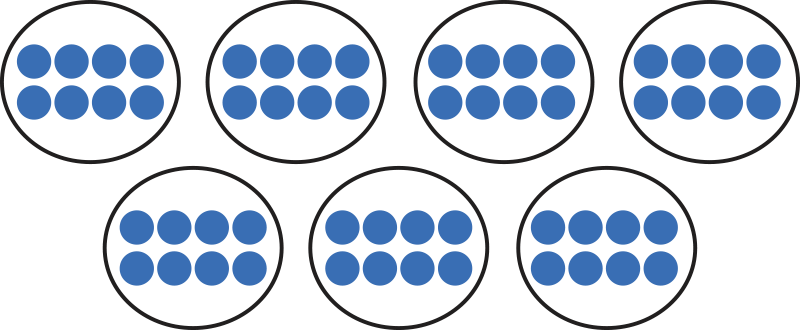
Correct! 7 \({ \times }\) 8 = 56 because each of the 7 circles has 8 dots. There are 56 dots in total!
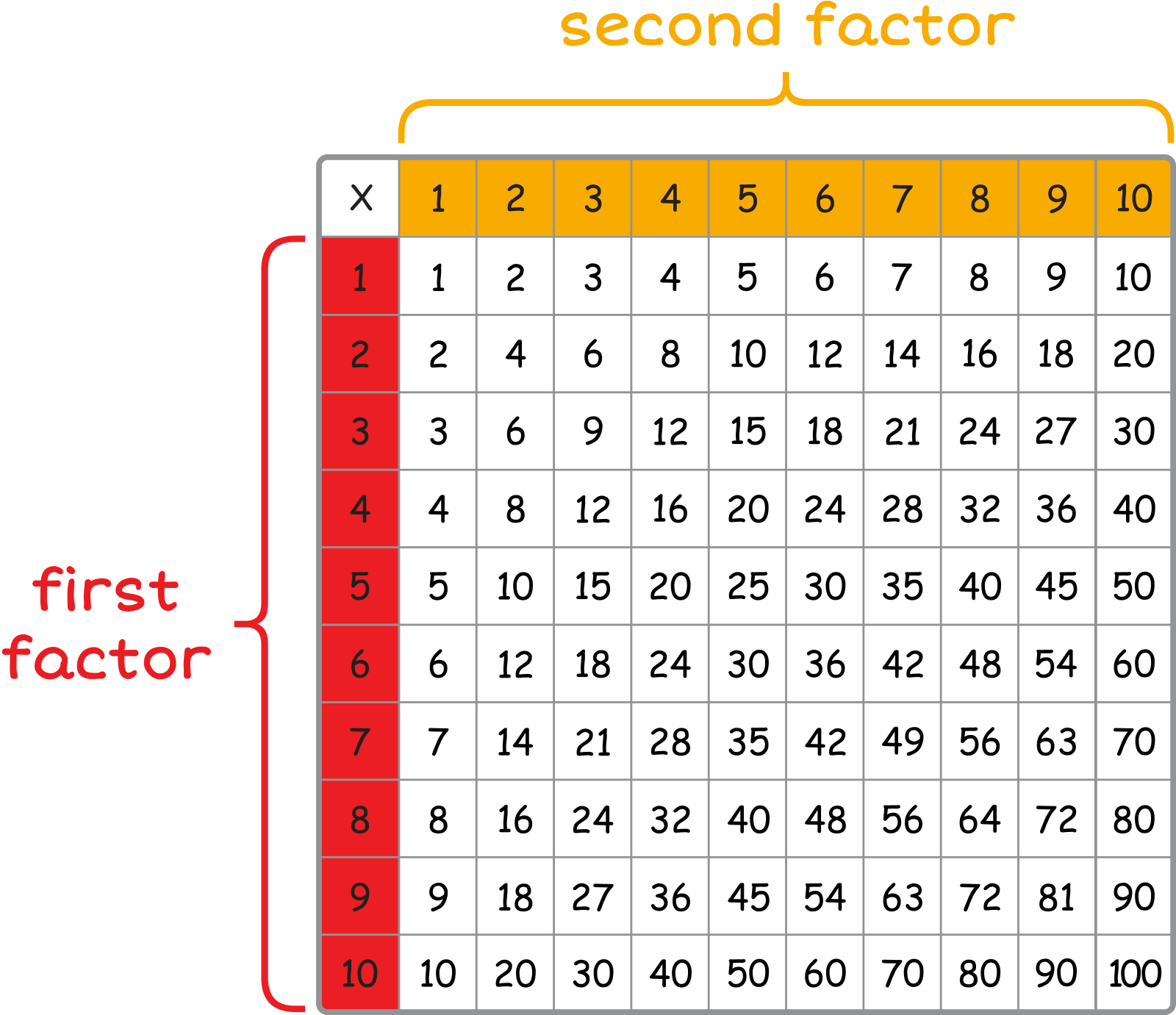
This is a multiplication table. The first factor is found in the first column. The second factor is in the first row. The product is where both factors meet in the table.
| 7 | |
| \({ \times }\) | 8 |
| ? |
Can you use the multiplication table to solve 7 \({ \times }\) 8? Click the Show Me button to check your answer.
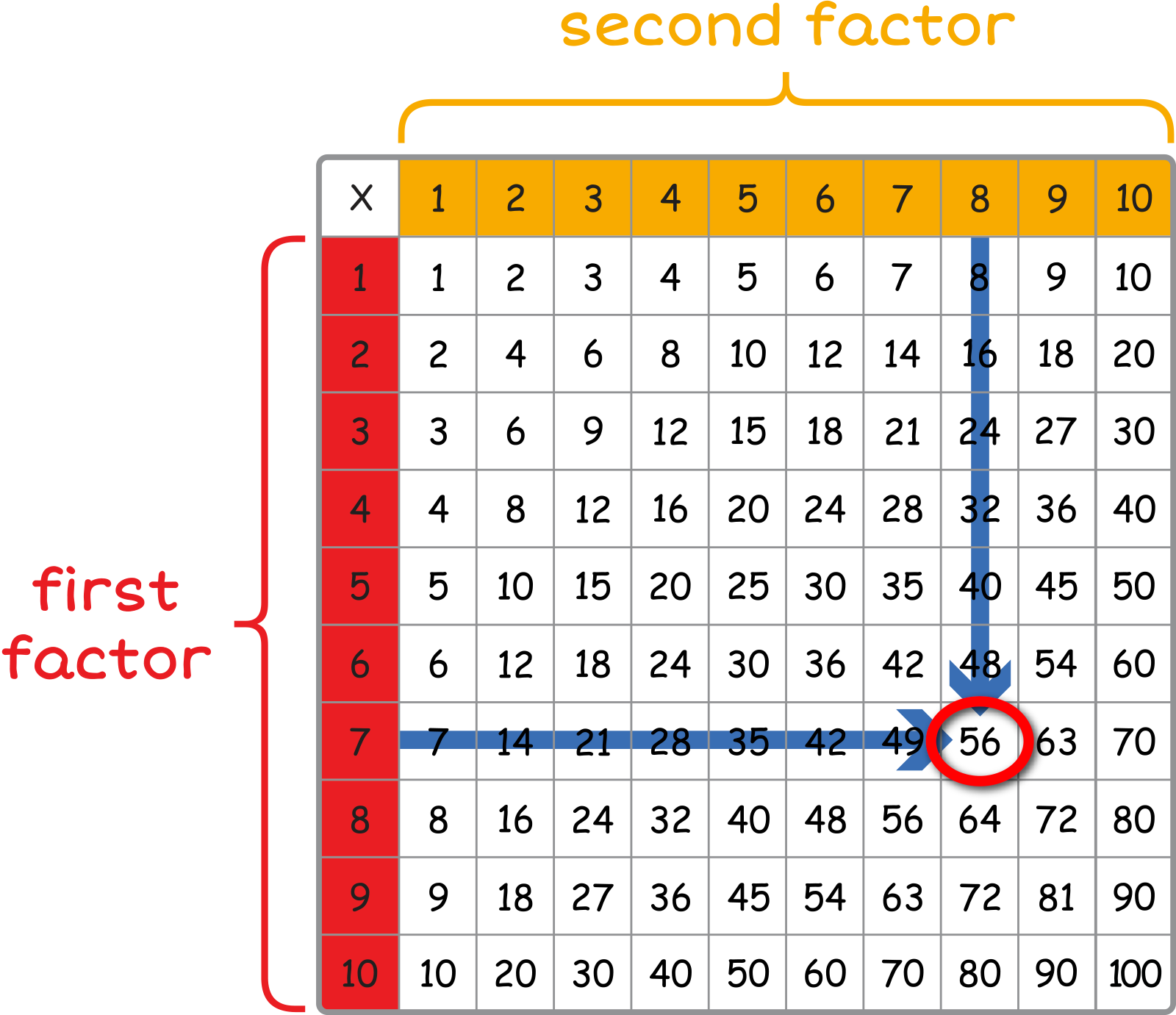
Good job! The product is 56 because that is where 7 and 8 meet in the multiplication table.
Each of these strategies helped us solve 7 \({ \times }\) 8. Great work!