 Circuit breakers are located in a circuit breaker box that is usually placed somewhere convenient in your house, such as on a wall just inside an attached garage, also at the point where the main line is divided up into different circuits.
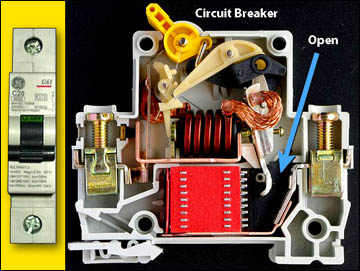
Circuit breakers are located in a circuit breaker box that is usually placed somewhere convenient in your house, such as on a wall just inside an attached garage, also at the point where the main line is divided up into different circuits.A circuit breaker works much the same way as a fuse. A circuit breaker is a switch with a gap in it. Because of the gap, no current flows through the switch under normal loads. The heat of a large electrical overload (caused by too many appliances operating at the same time) causes a bimetallic (two metal) strip within the circuit breaker to bend. When it bends, the metal strip becomes disconnected from the circuit. Electricity will arc, or jump, across the gap and activate the switch which immediately opens the circuit. When the metal strip cools sufficiently to be safely connected, the strip returns to its normal position. While a fuse must be replaced if it is blown, the circuit breaker only has to be reset and moved back into the “on” position after the overloading situation has been located and corrected. You must manually push the circuit breaker back to allow the electricity to flow again.
Circuit Breaker
What is an advantage of a circuit breaker over a fuse box?
A circuit breaker can be reset without having to replace the entire fuse or breaker. A switch is just flipped.
