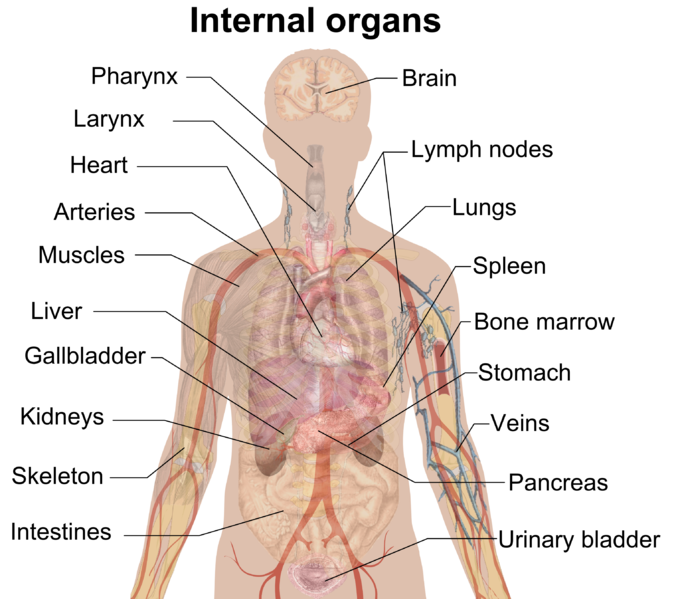
Humans and other animals that are bilaterally symmetrical do have some inconsistencies to their symmetries. That is, there are some asymmetries down the central axis--some parts are not exact mirror images. Take a look at the diagram of human organs. Can you see how there are some asymmetries down the central plane? List three or four features that are asymmetrical, then click the Show Me button to see how you did. Hint: make sure you name the left or right side from the model's perspective, not your perspective.

The heart is slightly left of the center. The liver is on the right, and the spleen is on the left. The gallbladder is on the right. The right kidney goes lower than the left kidney. The right lung has three lobes and the left lung has two lobes. The stomach swoops more to the left. Although not pictured, the appendix is on the right.
Animals have different body plans: asymmetric, radially symmetric, and bilaterally symmetric. In this video you will see some amazing animals and their symmetries. The video should also help you visualize how symmetries are determined.
![]() Symmetry is the correspondence in size, form, and arrangement of parts on opposite sides of a plane, line, or point; regularity of form or arrangement in terms of like, reciprocal, or corresponding parts. What does this have to do with Biology? Well, one way biologist can describe an animal is by its body plan which means the way the animal is shaped. All animal body plans fall under one of the following categories: asymmetrical, radially symmetrical, and bilaterally symmetrical. Asymmetrical means without symmetry or definite shape, or in other words irregular in form- like this sea sponge. Radially symmetrical means having symmetry that revolves around a central axis and from that center point, or in other words, there are numerous pieces that are equal and can be segmented- like this jellyfish and this sea urchin. Do you see how the sea urchin can be divided into equal pieces? Animals that are radially symmetrical have an oral and aboral side. The oral side is the side with the mouth. The aboral is the side without a mouth. Similar to how a pizza can be divided. Bilaterally symmetrical means having symmetry in which the arrangement of parts are on either side of a single central line that creates two equal mirror images on both sides- like this butterfly. Animals with bilateral symmetry are more complex. They have body parts with special functions to help the organism survive in its environment. Animals with bilateral symmetry have an anterior end, Posterior end, Ventral side, and Dorsal side. Bilateral symmetry lends itself to cephalization, which is the formation of a head or concentration of nervous tissue on the anterior end. What are some other benefits of each type of symmetry?
Symmetry is the correspondence in size, form, and arrangement of parts on opposite sides of a plane, line, or point; regularity of form or arrangement in terms of like, reciprocal, or corresponding parts. What does this have to do with Biology? Well, one way biologist can describe an animal is by its body plan which means the way the animal is shaped. All animal body plans fall under one of the following categories: asymmetrical, radially symmetrical, and bilaterally symmetrical. Asymmetrical means without symmetry or definite shape, or in other words irregular in form- like this sea sponge. Radially symmetrical means having symmetry that revolves around a central axis and from that center point, or in other words, there are numerous pieces that are equal and can be segmented- like this jellyfish and this sea urchin. Do you see how the sea urchin can be divided into equal pieces? Animals that are radially symmetrical have an oral and aboral side. The oral side is the side with the mouth. The aboral is the side without a mouth. Similar to how a pizza can be divided. Bilaterally symmetrical means having symmetry in which the arrangement of parts are on either side of a single central line that creates two equal mirror images on both sides- like this butterfly. Animals with bilateral symmetry are more complex. They have body parts with special functions to help the organism survive in its environment. Animals with bilateral symmetry have an anterior end, Posterior end, Ventral side, and Dorsal side. Bilateral symmetry lends itself to cephalization, which is the formation of a head or concentration of nervous tissue on the anterior end. What are some other benefits of each type of symmetry?
Question
What are the benefits of each type of symmetry?
