When the seasons change, so do we - we get out different clothing, do different sports and activities; we may even gain or lose body fat.

Lots of us adjust the thermostat in our homes when the season changes.
Humans aren't the only organisms that change their appearance and behavior when the season changes. Plants change as the seasons change, too - they just aren't always as obvious about it as humans are. Environmental factors like light have an enormous effect on plants. And, as the seasons change, a plant's physical appearance and behavior adjust to ensure the plant's survival in its new conditions.
Any change that occurs in a plant every year at about the same time of year is a seasonal change. In this lesson, we'll look at three types of seasonal changes in plants.
- Photoperiodism is the process that some plants use to flower at the same time every year.
-Dormancy is the process plants use to conserve energy during harsh conditions.
- Abscission is the process in which some trees lose their leaves every year.
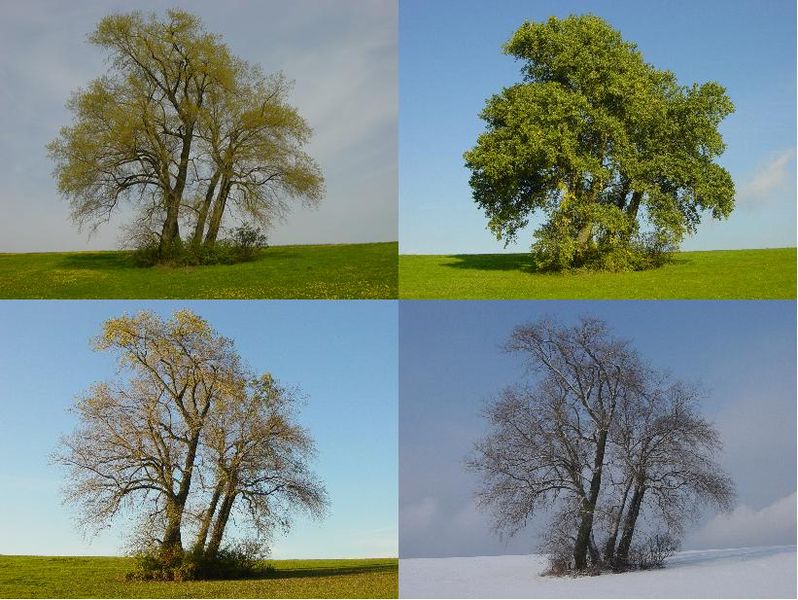

Poplar trees in four different seasons
A season is a part of the year that has a unique amount of daylight or precipitation. The picture shows a group of four poplar trees in four different seasons: spring, summer, fall, and winter. Not all places have four seasons, but many areas experience significant changes at different times of the calendar year. Some arctic areas experience polar day and night when the sun never fully rises or sets, while some tropical environments simply experience wet and dry seasons. In all of these climates, organisms - even plants - must adapt to the differences between seasons.
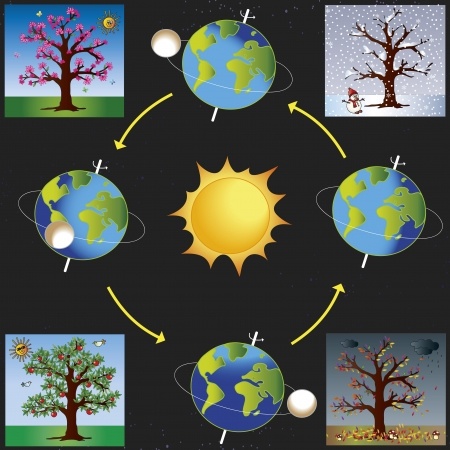
This image shows how seasons in the Earth's northern hemisphere are related to the way the earth is tilted on its axis.
Let's review what causes the seasons. Changes in weather, temperature, and precipitation are caused by the tilt of the Earth on its axis as it revolves around the sun. When a part of the Earth tilts toward the sun, it is summer in that area. Days are long, and nights are short, with the longest day being the summer solstice. When that part tilts away from the sun, it is winter in that area. Nights are long and days are short, with the winter solstice being the shortest day. One cycle of seasons is completed per year.
Review the examples of seasonal changes you've learned by completing the matching activity below.
|
dormancy
photoperiodism
abscission
|
the process in which some trees lose their leaves every year
the process that some plants use to flower at the same time every year
the process plants use to conserve energy during harsh conditions
|
Question
Besides sunlight, what other factors in a plant's environment change between seasons?
