When they divide to form new cells, somatic cells follow a rule that can be summarized this way: Like produces like. For instance, a cheek cell always divides into two identical cheek cells. The uniqueness of a cheek cell, or of any other somatic cell, lies in that cell's DNA. In other words, a cheek cell's DNA determines its ability to function as a cheek cell. DNA also ensures that the cheek cell can only divide into two new cheek cells--not any other kind of cell.
A cheek cell contains 46 distinct DNA strands, which exist as 46 chromosomes in its nucleus. (One chromosome contains one DNA.) Those 46 chromosomes, though, are actually 23 pairs of identical chromosomes. (These identical chromosomes are also known as chromatids.) For a cheek cell to divide into two new cheek cells with 46 chromosomes each, its DNA must be doubled. Before it divides, the cell must form enough new DNA to equal 92 chromatids (46 pairs).
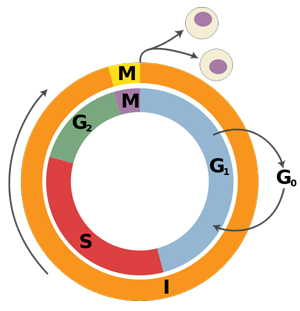
The doubling of chromosomes is a time-consuming and energy-demanding process. It occurs during the interphase of the cell cycle--the stage that includes the G1-S-G2 phases. As you click through this slide show, study each slide carefully to understand what happens in the beginning stages of the cell cycle.
|
When a cell begins to divide into two new cells, it leaves the G0 phase and enters the G1 phase. During the G1 phase, the cell prepares to divide and starts to grow and accumulate the molecules it will need to duplicate its DNA.
The actual replication of DNA happens in the S phase. When a single chromosome containing one strand of DNA divides itself into two new chromosomes, two identical copies of DNA are created. These copies are called sister chromatids (represented as an X). By the end of the S phase for a cheek cell, there will be 46 pairs of sister chromatids, or 92 chromatids in total.
In the G2 phase, the cell makes more proteins and gets ready to enter the M phase. |
Question
What is the most important thing that happens during the S phase of the cell cycle?