Many of the real-world problems that involve similar right triangles include a right triangle formed within another right triangle when an altitude is drawn from a vertex of the triangle to the opposite side.
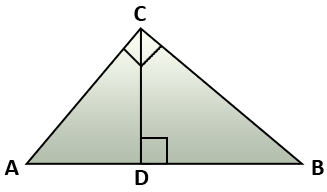
There are several rules that apply when an altitude is drawn inside a triangle:
1) \(\mathsf{ \Delta{}}\)CDB ~ \(\mathsf{ \Delta{}}\)ACB
2) \(\mathsf{ \Delta{}}\)ACD ~ \(\mathsf{ \Delta{}}\)ABC
3) \(\mathsf{ \Delta{}}\)CDB ~ \(\mathsf{ \Delta{}}\)ADC
Suppose you were trying to find the height of a roof that is sloped at a right angle.

The sides of the roof of a house measure 5 meters and 5 meters and the width of the house is 7.1 meters (1 meter is approximately 3.3 feet). How would you find the height of the roof?
First you would drop an imaginary altitude from the right angle on the vertex roof. Then you would use the similar right triangle created by the altitude (the one inside the triangle of the roof) to create a proportion that include the larger and the smaller triangle. Finally, you would simplify/solve the proportion.
Try solving the problem in your notebook. Then click the button below to check your work.

| \(\mathsf{ \frac{BD}{AB} = \frac{BC}{AC} }\) | We write the proportion. |
| \(\mathsf{ \frac{BD}{5} = \frac{5}{7.1} }\) | Substitute values from the problem. |
| 7.1BD = (5)(5) | Cross-multiply. |
| 7.1BD = 25 | Simplify. |
| BD = \(\mathsf{ \frac{25}{7.1} }\) = 3.5 | Simplify. |
So, the height of the roof would be 3.5 meters. (about 11.6 feet)
