Geometric means are special ratios that relate the sides of similar right triangles. While geometric means don't apply to every situation, if a problem involves right triangles with altitudes and you need to find out how the legs, hypotenuse, and altitudes are related, the geometric mean can be the best approach. It's also helpful for solving problems based on similar right triangles when the ratios between the sides of a triangle are known or can be easily determined.
There are two basic rules to remember when applying geometric means.
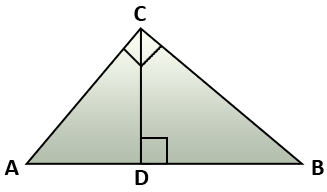
The Altitude Rule: If you have a triangle ABC with altitude CD, then you can use the altitude as the geometric mean between the segments of the hypotenuse created by the altitude. As a result, you can write the proportion \(\mathsf{ \frac{BD}{CD} = \frac{CD}{AD} }\).
The Leg Rule: Consider each leg of the triangle ABC as the geometric mean between the hypotenuse and the closest projection to the leg. In this way, you can create the useful proportion \(\mathsf{ \frac{AB}{AC} = \frac{AC}{AD} }\).
How do you actually use these rules? Let's look at a typical real-world problem related to geometric mean.
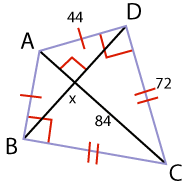 Let's say that you are constructing a kite, based on directions you found online. Unfortunately, a key piece of information was left out of the instructions--the length of the wooden dowel you'll need to create the crossbar (shown here as BD). You need to figure out the length of BD, given the size of the triangles forming the kite's paper "body." Hint: You'll need to find the length of DX, and then double it.
Let's say that you are constructing a kite, based on directions you found online. Unfortunately, a key piece of information was left out of the instructions--the length of the wooden dowel you'll need to create the crossbar (shown here as BD). You need to figure out the length of BD, given the size of the triangles forming the kite's paper "body." Hint: You'll need to find the length of DX, and then double it.
Reread the scenario to make sure you understand what information you need to find. Then click each step below to see how to solve this problem. Notice how several solutions are systematically ruled out.
| Step 1 | Since DX is an altitude, you could apply the altitude rule or the leg rule. Based on the information in the problem, which rule should you use? |
| Step 2 | Look at the information you have already: 84 as the hypotenuse, 72 as the longest leg, and 44 as the shortest leg of the big triangle ADC. |
| Step 3 | The altitude rule deals with the two segments that form the hypotenuse. This is not the rule to use because you don't know anything about the line segments. Use the leg rule instead. |
| Step 4 | Choose either one of the legs, say AD. This will help find the two segments that form the hypotenuse. |
| Step 5 | To solve the problem, create a ratio based on the Leg Rule, and solve. \(\mathsf{ \frac{AX}{AD} = \frac{AD}{AC} }\) \(\mathsf{ \frac{AX}{44} = \frac{44}{84} }\) 84(AX) = (44)(44) 84(AX) = 1936 AX = \(\mathsf{ \frac{1936}{84} }\) = 23 So AX = 23 and XC = 84 − 23 = 61 |
| Step 6 | Now DX is the geometric mean between the two segments of the hypotenuse (Altitude Rule). \(\mathsf{ \frac{23}{DX} = \frac{DX}{61} }\) \(\mathsf{ (DX)^{2} = (23)(61) }\) \(\mathsf{ \sqrt{ (DX)^{2} } = \sqrt{ 1403 } }\) \(\mathsf{ DX = 37.5 }\) The crossbar of the kite should be 2(DX) = 2(37.5) = 75 |
