Besides having most body parts in common (visceral mass, mantle, foot, coelom, radula, and foot), mollusks all have the same five organ systems. An organ system is a group of organs that work for a common task. These organ systems are highly specialized and are only found in very complex animals.
Click through the activity below to learn about the five organ systems that all mollusks have.
Digestive
Circulatory
Excretory
Respiratory
Reproductive
![By Original by Al2, English captions and other edits by Jeff Dahl (Own work) [GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html) or CC-BY-SA-3.0-2.5-2.0-1.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons]](https://s3.amazonaws.com/cms.accelerate-ed.com/image/ab5d351e-0e9c-4cc0-868f-5047b520ed04.jpg)
The digestive organs are located within the visceral mass of the mollusk body. Mollusks with a radula stick it out to scrape food off different surfaces like leaves and rocks. They then return the radula to their mouth, carrying the food with it. The food is swallowed and goes down their digestive tract (colored in green in the picture). The food is broken down and the nutrients are taken up by the cells lining the digestive tract. These cells then transport the nutrients to the blood.
Some mollusks, bivalves, lack a radula. Instead, bivalves have cilia that they use to pull water over their gills. Their gills are coated in a mucus that catches small organisms and food particles. The captured prey then flow into their mouth and through the digestive tract.
Digested food then exits the mollusk body through the anus, a pore on the outside of the mollusk's body.
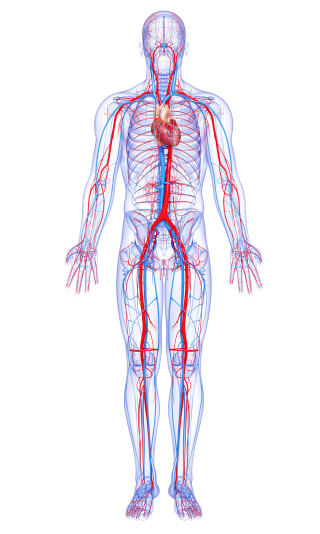
Pictured is the human circulatory system, which features closed circulation. Notice how the blood is contained within vessels.
The purpose of the circulatory system is to carry nutrients and oxygen to all the cells within the body. Most mollusks have an open circulatory system, which means there is blood in the body cavity (coelom) that bathes the organs with the necessary nutrients and oxygen. This is different from more complex animals that have closed circulatory systems where all the blood is contained within vessels such as veins, arteries, and capillaries. The only mollusks with closed circulatory systems are squid and octopus.
What is the difference between open and closed circulatory systems? Think of the answer, then click "Show Me" to see if you are correct.

Open circulatory systems have blood within the coelom, and the organs are bathed in nutrients and oxygen. Closed circulatory systems contain blood within blood vessels such as arteries, veins, and capillaries.
All mollusks have a three-chambered heart, which means their heart has three distinct regions, as opposed to humans, which have a four-chambered heart. The heart pumps the blood to the body cavity when it is oxygenated, and when the blood no longer has oxygen, it is pumped to the lung to get more oxygen.
![By KDS444 (Own work) [CC-BY-SA-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://s3.amazonaws.com/cms.accelerate-ed.com/image/5f7e72e9-cab4-42bf-9ddb-d68d89c3e7b8.jpg)
The excretory system is involved in releasing liquid waste from the body. The fluid waste is collected within the coelom and then pulled into a tube called a nephridia, where nutrients are absorbed back into the mollusk tissue. Nephridia comes from the Greek word nephros for kidney. The remaining fluid waste exits the nephridia through a pore and is then dumped into the mantle cavity where it is released from the body.
What is the purpose of the excretory system? Think of the answer, then click "Show Me" to see if you are correct.

The excretory system is in charge of getting rid of liquid waste from the body.
Squid live in water, therefore they have gills that take up oxygen.
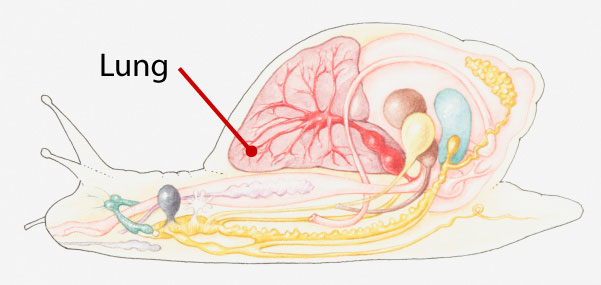
Snails are terrestrial mollusks, therefore they have lungs to take in oxygen.
The respiratory system specializes in taking in oxygen from the environment. It works closely with the circulatory system to transport oxygen to all the tissues in the body.
All the mollusks that live in water have gills, which are located within the mantle cavity. Water passes over the gills, bringing with it oxygen. The oxygen is then taken up by the gills and transported to the blood to be carried to all the cells in the mollusk's body.
In mollusks that are terrestrial, that is, live on land, there is a simple lung rather than gills. The lung is also located within the mantle cavity. The lung is very delicate and must be kept moist in order to take in oxygen properly, so terrestrial mollusks tend to be more active at night or after a rain storm when the air is moist. During particularly dry times, terrestrial mollusks secrete a thick mucus that creates a plug to block any openings in their body to conserve moisture.
How are mollusks that live in water different from mollusks that live on land when it comes to their respiratory organs? Think of the answer, then click "Show Me" to see if you are correct.

Mollusks that live in saltwater and freshwater environments have gills that specialize in taking in oxygen, whereas terrestrial mollusks have a simple lung that takes in oxygen.
![By Daniel J Jackson, Gert Wörheide and Bernard M Degnan [CC-BY-2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://s3.amazonaws.com/cms.accelerate-ed.com/image/d9fc4631-147b-4fb9-9e05-88afee24e671.jpg)
Some mollusks are hermaphrodites--individuals that produce both eggs and sperm. Other mollusks are individual males and females. Some oysters and slugs don't stick to one particular gender but rather switch back and forth between being male and female. All mollusks engage in sexual reproduction. Recall that in sexual reproduction, male sperm fertilize female eggs.
Some mollusks release their gametes (eggs and sperm) into the water for fertilization to occur. Some terrestrial mollusks and cephalopods release sperm into the female internally for internal fertilization.
All mollusk fertilized eggs develop into a trochophore, as pictured. The trochophore is a larval stage in mollusk development. Recall that the larval stage is a developmental stage that occurs after fertilization. The trochophore is covered in cilia so that it can swim freely.
What larval stage do all mollusks have in common? Think of the answer, then click "Show Me" to see if you are correct.

All mollusks have a trochophore larval stage.
Jot down an answer to each of these questions--or say the answer to yourself--before clicking the question to check your understanding of mollusk organ systems.
| What is the common larval stage among all mollusks, and what feature helps it swim? | All mollusks share the trochophore larval stage. Mollusk larva have cilia to help them swim. |
| What is the name of the organ in some mollusks that scrapes rocks and plants for food? | The radula is the tongue-like structure that scrapes food off different surfaces. |
| What is the purpose of the nephridia? | The nephridia captures liquid waste from the coelom. It is where nutrients can be reabsorbed before the waste is released out of the body. |
| How are the breathing structures in mollusks that live in water different from the breathing structures in mollusks that live on land? | Mollusks that live in water breathe in through gills, whereas mollusks that live on land have a simple lung. |
| What is the difference between open and closed circulation? | Open circulation occurs when the organs are bathed in blood inside the body cavity, while closed circulation occurs when the blood is enclosed in blood vessels. |
