A quadratic equation is an equation whose largest exponent is 2. The standard form of a quadratic equation is \( ax^{2} + bx + c = 0 \), where a, b, and c are numbers. In order to solve a quadratic equation for x, it helps if the equation is expressed in standard form. When a quadratic equation is expressed in standard form, you can easily identify the values of a, b, and c.
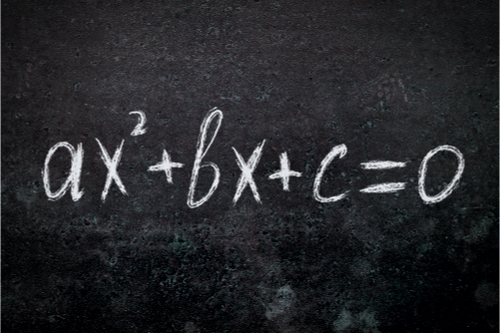
Write the equation \( x^{2} + 8x = - 12 \) in standard form. Then identify the values of a, b, and c.
A quadratic equation is in standard form when its structure matches \( ax^{2} + bx + c = 0 \). |
The given quadratic equation is not equal to 0. Rewrite the equation by adding 12 to both sides. \( x^{2} + 8x = - 12 \) \( x^{2} + 8x + 12 = 0 \) Now the quadratic equation is written in standard form. |
Read the values of a, b, and c from the standard form of the quadratic equation. |
\( a = 1 \) \( b = 8 \) \( c = 12 \) |
Use the activity below to practice writing quadratic equations in standard form. Click each equation and write it in standard form. Once the quadratic equation is written in standard form, identify the values of a, b, and c. Click the equation to check your answer.
