 The body also uses positive feedback loops to maintain homeostasis. |
Thermoregulation and blood glucose levels are just two of many systems in which the output signals the pathway to stop. Less common, but no less important to homeostasis, are positive feedback loops. A positive feedback loop occurs when the effect of a pathway is picked up by the sensor and the sensor tells the system to start the pathway over again.
For instance, when a microphone gets too close to a speaker, you might hear a screeching noise, which causes a positive feedback loop. The speaker emits a noise that is picked up by the microphone. That sound then goes through the sound system and comes out through the speaker. That noise is picked up through the microphone, but it's stronger this time. This pattern continues, with each cycle getting louder and louder until someone puts a stop to it.
What are the roles of the microphone and the speaker in this positive feedback system? First, write down or think about the answer to this question. Then click the Answer button to check your answer.
The microphone is the sensor; the speaker is the effector.
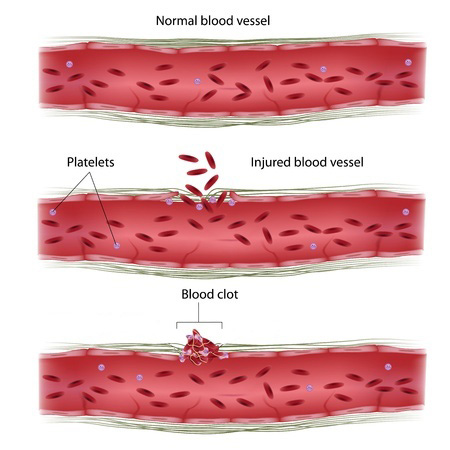 Injured blood vessels stop bleeding through a positive feedback mechanism. |
Blood clotting happens because of a positive feedback mechanism. When you get a cut, blood cells called platelets gather around the wound to help fill the hole and stop the bleeding. These cells release a chemical that attracts more platelets. The cycle of more platelets and more chemical continues until the cut is sufficiently closed and the bleeding stops.
Another example of a positive feedback mechanism occurs in the contractions of childbirth. During childbirth, the muscles of the uterus cramp and, in the process, release a hormone that, in turn, causes more and stronger muscle cramps. This positive feedback ends when the child is born, and no more hormone is released.
Question
What is the purpose of a negative feedback loop and how do negative and positive feedback loops differ from one another?
